Dielectrophoresis for Biomedical Sciences Applications: A Review
- PMID: 28245552
- PMCID: PMC5375735
- DOI: 10.3390/s17030449
Dielectrophoresis for Biomedical Sciences Applications: A Review
Abstract
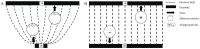
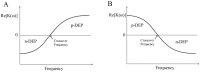
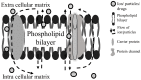
Dielectrophoresis (DEP) is a label-free, accurate, fast, low-cost diagnostic technique that uses the principles of polarization and the motion of bioparticles in applied electric fields. This technique has been proven to be beneficial in various fields, including environmental research, polymer research, biosensors, microfluidics, medicine and diagnostics. Biomedical science research is one of the major research areas that could potentially benefit from DEP technology for diverse applications. Nevertheless, many medical science research investigations have yet to benefit from the possibilities offered by DEP. This paper critically reviews the fundamentals, recent progress, current challenges, future directions and potential applications of research investigations in the medical sciences utilizing DEP technique. This review will also act as a guide and reference for medical researchers and scientists to explore and utilize the DEP technique in their research fields.
Keywords: biomedical sciences; diagnostic; dielectrophoresis; point-of-care.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Caliendo A.M., Gilbert D.N., Ginocchio C.C., Hanson K.E., May L., Quinn T.C., Tenover F.C., Alland D., Blaschke A.J., Bonomo R.A., et al. Better tests, better care: Improved diagnostics for infectious diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013;57(Suppl. S3):S139–S170. doi: 10.1093/cid/cit578. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

