Targeting Splicing in the Treatment of Human Disease
- PMID: 28245575
- PMCID: PMC5368691
- DOI: 10.3390/genes8030087
Targeting Splicing in the Treatment of Human Disease
Abstract
The tightly regulated process of precursor messenger RNA (pre-mRNA) alternative splicing (AS) is a key mechanism in the regulation of gene expression. Defects in this regulatory process affect cellular functions and are the cause of many human diseases. Recent advances in our understanding of splicing regulation have led to the development of new tools for manipulating splicing for therapeutic purposes. Several tools, including antisense oligonucleotides and trans-splicing, have been developed to target and alter splicing to correct misregulated gene expression or to modulate transcript isoform levels. At present, deregulated AS is recognized as an important area for therapeutic intervention. Here, we summarize the major hallmarks of the splicing process, the clinical implications that arise from alterations in this process, and the current tools that can be used to deliver, target, and correct deficiencies of this key pre-mRNA processing event.
Keywords: alternative splicing; genetic disease; precursor messenger RNA; therapy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
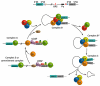

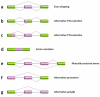
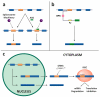
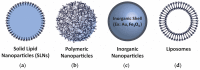
References
-
- Consortium IHGS Finishing the euchromatic sequence of the human genome. Nature. 2004;431:931–945. - PubMed
-
- The Human Proteome Map. [(accessed on 16 December 2016)]. Available online: www.humanproteomemap.org.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

