Molecular Imprinting Technology in Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Sensors
- PMID: 28245588
- PMCID: PMC5375740
- DOI: 10.3390/s17030454
Molecular Imprinting Technology in Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) Sensors
Abstract
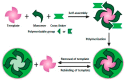
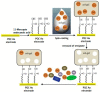
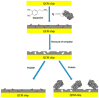
Molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs) as artificial antibodies have received considerable scientific attention in the past years in the field of (bio)sensors since they have unique features that distinguish them from natural antibodies such as robustness, multiple binding sites, low cost, facile preparation and high stability under extreme operation conditions (higher pH and temperature values, etc.). On the other hand, the Quartz Crystal Microbalance (QCM) is an analytical tool based on the measurement of small mass changes on the sensor surface. QCM sensors are practical and convenient monitoring tools because of their specificity, sensitivity, high accuracy, stability and reproducibility. QCM devices are highly suitable for converting the recognition process achieved using MIP-based memories into a sensor signal. Therefore, the combination of a QCM and MIPs as synthetic receptors enhances the sensitivity through MIP process-based multiplexed binding sites using size, 3D-shape and chemical function having molecular memories of the prepared sensor system toward the target compound to be detected. This review aims to highlight and summarize the recent progress and studies in the field of (bio)sensor systems based on QCMs combined with molecular imprinting technology.
Keywords: biomolecular recognition; biosensors; molecularly imprinted polymers (MIPs); quartz crystal microbalance (QCM); synthetic receptors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
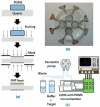
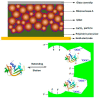
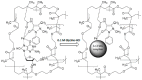

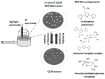
Similar articles
-
Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Quartz Crystal Microbalance Sensor for the Clinical Detection of Insulin.Methods Mol Biol. 2021;2359:209-222. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1629-1_18. Methods Mol Biol. 2021. PMID: 34410672
-
Preparation of a molecularly imprinted sensor based on quartz crystal microbalance for specific recognition of sialic acid in human urine.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018 Jul;410(18):4387-4395. doi: 10.1007/s00216-018-1094-7. Epub 2018 May 8. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29736700
-
Oriented surface epitope imprinted polymer-based quartz crystal microbalance sensor for cytochrome c.Talanta. 2019 Jan 1;191:222-228. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.079. Epub 2018 Aug 29. Talanta. 2019. PMID: 30262054
-
Label-Free Bioanalyte Detection from Nanometer to Micrometer Dimensions-Molecular Imprinting and QCMs †.Biosensors (Basel). 2018 Jun 1;8(2):52. doi: 10.3390/bios8020052. Biosensors (Basel). 2018. PMID: 29865200 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Electrochemical MIP-Sensors for Drugs.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(33):4007-4019. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666171005103712. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28982312 Review.
Cited by
-
Selective Recognition of Myoglobin in Biological Samples Using Molecularly Imprinted Polymer-Based Affinity Traps.Int J Anal Chem. 2018 Aug 8;2018:4359892. doi: 10.1155/2018/4359892. eCollection 2018. Int J Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 30174693 Free PMC article.
-
Research trends of piezoelectric materials in neurodegenerative disease applications.Bioact Mater. 2025 Jun 13;52:366-392. doi: 10.1016/j.bioactmat.2025.06.022. eCollection 2025 Oct. Bioact Mater. 2025. PMID: 40585388 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selective Adsorption and Purification of the Acteoside in Cistanche tubulosa by Molecularly Imprinted Polymers.Front Chem. 2020 Jan 23;7:903. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2019.00903. eCollection 2019. Front Chem. 2020. PMID: 32039143 Free PMC article.
-
Exploration of PVC@SiO2 nanostructure for adsorption of methylene blue via using quartz crystal microbalance technology.Sci Rep. 2023 Nov 10;13(1):19621. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-46807-4. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37949908 Free PMC article.
-
Affinity Sensing Strategies for the Detection of Pesticides in Food.Foods. 2018 Sep 5;7(9):148. doi: 10.3390/foods7090148. Foods. 2018. PMID: 30189666 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cheremisinoff P. Advances in Environmental Control Technology: Health and Toxicology. Gulf Professional Publishing; Houston, TX, USA: 1997.
-
- Sellergren B. Molecularly Imprinted Polymers: Man-Made Mimics of Antibodies and Their Application in Analytical Chemistry: Techniques and Instrumentation in Analytical Chemistry. Elsevier Science; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2001.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

