A UPLC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Free and Total Forms of a Phenolic Acid and Two Flavonoids in Rat Plasma and Its Application to Comparative Pharmacokinetic Studies of Polygonum capitatum Extract in Rats
- PMID: 28245598
- PMCID: PMC6155221
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules22030353
A UPLC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Determination of Free and Total Forms of a Phenolic Acid and Two Flavonoids in Rat Plasma and Its Application to Comparative Pharmacokinetic Studies of Polygonum capitatum Extract in Rats
Abstract
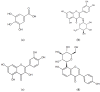
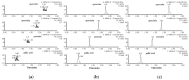
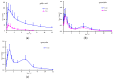
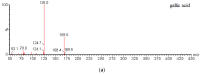
The principal active constituents of Polygonum capitatum are phenolic acids and flavonoids, such as gallic acid, quercitrin, and quercetin. The aim of this study was to develop and validate a method to determine the three constituents and the corresponding conjugated metabolites of Polygonum capitatum in vivo and to conduct pharmacokinetic studies on the herb, a well-known Miao medicinal plant in China. Gallic acid, quercitrin, and quercetin were analysed by ultra-performance liquid chromatography-electrospray ionization-tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS/MS). Protein precipitation in plasma samples was performed using methanol. For the determination of total forms of analytes, an additional process of hydrolysis was conducted using β-glucuronidase and sulphatase. The analytes were separated on a BEH C18 column (50 mm × 2.1 mm; i.d., 1.7 μm) and quantified by multiple reaction monitoring (MRM) mode. The linear regression showed high linearity over a 729-fold dynamic range for the three analytes. The relative standard deviations of intra- and inter-day measurements were less than 9.5%, and the method was accurate to within -11.1% to 12.5%. The extraction recoveries for gallic acid, quercitrin, and quercetin were 94.3%-98.8%, 88.9%-98.8%, and 95.7%-98.5%, respectively. All samples were stable under short- and long-term storage conditions. The validated method was successfully applied to a comparative pharmacokinetic study of gallic acid, quercitrin, and quercetin in their free and total forms in rat plasma. The study revealed significantly higher exposure of the constituents in total forms for gallic acid and quercetin, while quercitrin was detected mainly in its corresponding free form in vivo. The established method was rapid and sensitive for the simultaneous quantification of free and total forms of multiple constituents of Polygonum capitatum extract in plasma.
Keywords: Polygonum capitatum extract; UPLC-ESI-MS/MS; flavonoids; hydrolysis; pharmacokinetics; phenolic acids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Simultaneous determination of four bioactive flavonoids from Polygonum orientale L. in dog plasma by UPLC-ESI-MS/MS and application of the technique to pharmacokinetic studies.J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014 Apr 15;957:96-104. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2014.02.055. Epub 2014 Mar 12. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24662144
-
An UHPLC-MS/MS method for simultaneous quantification of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid in rat plasma after oral administration of Polygonum capitatum extract and its application to pharmacokinetics.J Ethnopharmacol. 2015 Mar 13;162:377-83. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2014.12.044. Epub 2014 Dec 31. J Ethnopharmacol. 2015. PMID: 25557034
-
Comparative Pharmacokinetics of Gallic Acid, Protocatechuic Acid, and Quercitrin in Normal and Pyelonephritis Rats after Oral Administration of a Polygonum capitatum Extract.Molecules. 2019 Oct 27;24(21):3873. doi: 10.3390/molecules24213873. Molecules. 2019. PMID: 31717895 Free PMC article.
-
Polygonum capitatum, the Hmong Medicinal Flora: A Comprehensive Review of Its Phytochemical, Pharmacological and Pharmacokinetic Characteristics.Molecules. 2022 Sep 28;27(19):6407. doi: 10.3390/molecules27196407. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36234943 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers for exposure to dietary flavonoids: a review of the current evidence for identification of quercetin glycosides in plasma.Br J Nutr. 2001 Aug;86 Suppl 1:S105-10. doi: 10.1079/bjn2001342. Br J Nutr. 2001. PMID: 11520427 Review.
Cited by
-
A High Performance Thin Layer Chromatographic Method Using a Design of Experiment Approach for Estimation of Phytochemicals in Extracts of Moringa Oleifera Leaves.Turk J Pharm Sci. 2020 Apr;17(2):148-158. doi: 10.4274/tjps.galenos.2018.80958. Epub 2020 Apr 24. Turk J Pharm Sci. 2020. PMID: 32454774 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacokinetics of gallic acid and protocatechuic acid in humans after dosing with Relinqing (RLQ) and the potential for RLQ-perpetrated drug-drug interactions on organic anion transporter (OAT) 1/3.Pharm Biol. 2021 Dec;59(1):757-768. doi: 10.1080/13880209.2021.1934039. Pharm Biol. 2021. PMID: 34144662 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Quercetin from Polygonum capitatum Protects against Gastric Inflammation and Apoptosis Associated with Helicobacter pylori Infection by Affecting the Levels of p38MAPK, BCL-2 and BAX.Molecules. 2017 May 6;22(5):744. doi: 10.3390/molecules22050744. Molecules. 2017. PMID: 28481232 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of Antioxidant Activity and Biotransformation of Opuntia Ficus Fruit: The Effect of In Vitro and Ex Vivo Gut Microbiota Metabolism.Molecules. 2022 Nov 4;27(21):7568. doi: 10.3390/molecules27217568. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36364395 Free PMC article.
-
Combined transcriptomic and metabolomic analyses reveal the pharmacognostic mechanism of the metabolism of flavonoids in different parts of Polygonum capitatum.Plant Genome. 2025 Mar;18(1):e20543. doi: 10.1002/tpg2.20543. Plant Genome. 2025. PMID: 39807534 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Editorial Committee of Chinese Materia Medica, State Administration of TCM . Miao’s Material Medica, Chinese Materia Medica (Zhonghua Bencao) Publishier of Guizhou Science and Technology; Guiyang, China: 2005. pp. 223–224.
-
- Editorial Committee of Chinese Pharmacopoeia . Chinese Pharmacopoeia. China Medical Science and Technology Press; Beijing, China: 2010. p. 992.
-
- Li Y.-M., Gong Y. The research progress on the chemical component and the pharmacology of polygotum capitatum ham ex d. Don. J. Guizhou Univ. (Nat. Sci.) 2007;24:205–207.
-
- Liu M., Luo C.-L., Zhang Y.-P., Qiu D.-W. Analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and diuretic effects of polygonum capitatum and toddalia asiatica. Guizhou Med. J. 2007;31:370–371.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

