Gene Expression in Osteolysis: Review on the Identification of Altered Molecular Pathways in Preclinical and Clinical Studies
- PMID: 28245614
- PMCID: PMC5372515
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms18030499
Gene Expression in Osteolysis: Review on the Identification of Altered Molecular Pathways in Preclinical and Clinical Studies
Abstract
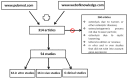
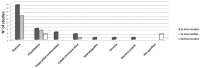
Aseptic loosening (AL) due to osteolysis is the primary cause of joint prosthesis failure. Currently, a second surgery is still the only available treatment for AL, with its associated drawbacks. The present review aims at identifying genes whose expression is altered in osteolysis, and that could be the target of new pharmacological treatments, with the goal of replacing surgery. This review also aims at identifying the molecular pathways altered by different wear particles. We reviewed preclinical and clinical studies from 2010 to 2016, analyzing gene expression of tissues or cells affected by osteolysis. A total of 32 in vitro, 16 in vivo and six clinical studies were included. These studies revealed that genes belonging to both inflammation and osteoclastogenesis pathways are mainly involved in osteolysis. More precisely, an increase in genes encoding for the following factors were observed: Interleukins 6 and 1β (IL16 and β), Tumor Necrosis Factor α (TNFα), nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells (NFκB), Nuclear factor of activated T-cells, cytoplasmic 1 (NFATC1), Cathepsin K (CATK) and Tartrate-resistant acid phosphatase (TRAP). Titanium (Ti) and Polyethylene (PE) were the most studied particles, showing that Ti up-regulated inflammation and osteoclastogenesis related genes, while PE up-regulated primarily osteoclastogenesis related genes.
Keywords: aseptic loosening; gene expression; genomics; inflammation; osteoclastogenesis; osteolysis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Piperlongumine Inhibits Titanium Particles-Induced Osteolysis, Osteoclast Formation, and RANKL-Induced Signaling Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Mar 5;23(5):2868. doi: 10.3390/ijms23052868. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35270008 Free PMC article.
-
Scutellarin inhibits RANKL-mediated osteoclastogenesis and titanium particle-induced osteolysis via suppression of NF-κB and MAPK signaling pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2016 Nov;40:458-465. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2016.09.031. Epub 2016 Oct 8. Int Immunopharmacol. 2016. PMID: 27728897
-
Particle-induced SIRT1 downregulation promotes osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis through ER stress regulation.Biomed Pharmacother. 2018 Aug;104:300-306. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2018.05.030. Epub 2018 May 25. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018. PMID: 29775898
-
Rhoifolin ameliorates titanium particle-stimulated osteolysis and attenuates osteoclastogenesis via RANKL-induced NF-κB and MAPK pathways.J Cell Physiol. 2019 Aug;234(10):17600-17611. doi: 10.1002/jcp.28384. Epub 2019 Mar 10. J Cell Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30854667
-
Mechanism of regulating macrophages/osteoclasts in attenuating wear particle-induced aseptic osteolysis.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 4;14:1274679. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1274679. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37860014 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Ibudilast Mitigates Delayed Bone Healing Caused by Lipopolysaccharide by Altering Osteoblast and Osteoclast Activity.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Jan 25;22(3):1169. doi: 10.3390/ijms22031169. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33503906 Free PMC article.
-
Bone regeneration is associated with the concentration of tumour necrosis factor-α induced by sericin released from a silk mat.Sci Rep. 2017 Nov 14;7(1):15589. doi: 10.1038/s41598-017-15687-w. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 29138464 Free PMC article.
-
Fibroblast-Like-Synoviocytes Mediate Secretion of Pro-Inflammatory Cytokines via ERK and JNK MAPKs in Ti-Particle-Induced Osteolysis.Materials (Basel). 2020 Aug 17;13(16):3628. doi: 10.3390/ma13163628. Materials (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32824426 Free PMC article.
-
[Establishment of artificial joint aseptic loosening mouse model by cobalt-chromium particles stimulation].Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020 May 15;34(5):615-620. doi: 10.7507/1002-1892.201909023. Zhongguo Xiu Fu Chong Jian Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2020. PMID: 32410430 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
NFATc1 is a tumor suppressor in hepatocellular carcinoma and induces tumor cell apoptosis by activating the FasL-mediated extrinsic signaling pathway.Cancer Med. 2018 Sep;7(9):4701-4717. doi: 10.1002/cam4.1716. Epub 2018 Aug 7. Cancer Med. 2018. PMID: 30085405 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cordova L.A., Stresing V., Gobin B., Rosset P., Passuti N., Gouin F., Trichet V., Layrolle P., Heymann D. Orthopaedic implant failure: Aseptic implant loosening—The contribution and future challenges of mouse models in translational research. Clin. Sci. 2014;127:277–293. doi: 10.1042/CS20130338. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous