Effects of sarcosine and N, N-dimethylglycine on NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory field potentials
- PMID: 28245819
- PMCID: PMC5331637
- DOI: 10.1186/s12929-016-0314-8
Effects of sarcosine and N, N-dimethylglycine on NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory field potentials
Abstract
Background: Sarcosine, a glycine transporter type 1 inhibitor and an N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor co-agonist at the glycine binding site, potentiates NMDA receptor function. Structurally similar to sarcosine, N,N-dimethylglycine (DMG) is also N-methyl glycine-derivative amino acid and commonly used as a dietary supplement. The present study compared the effects of sarcosine and DMG on NMDA receptor-mediated excitatory field potentials (EFPs) in mouse medial prefrontal cortex brain slices using a multi-electrode array system.
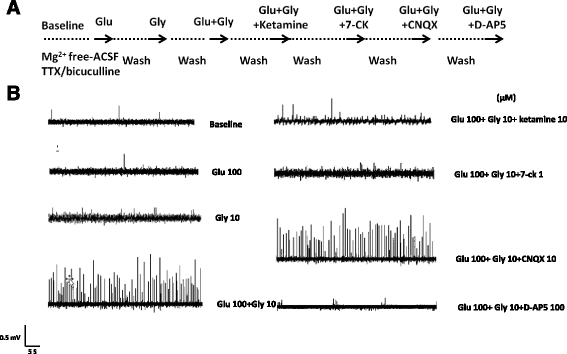
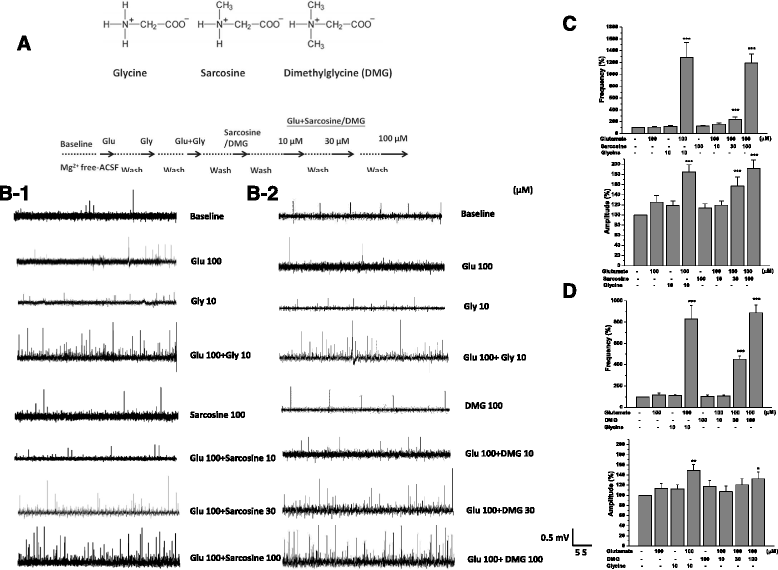
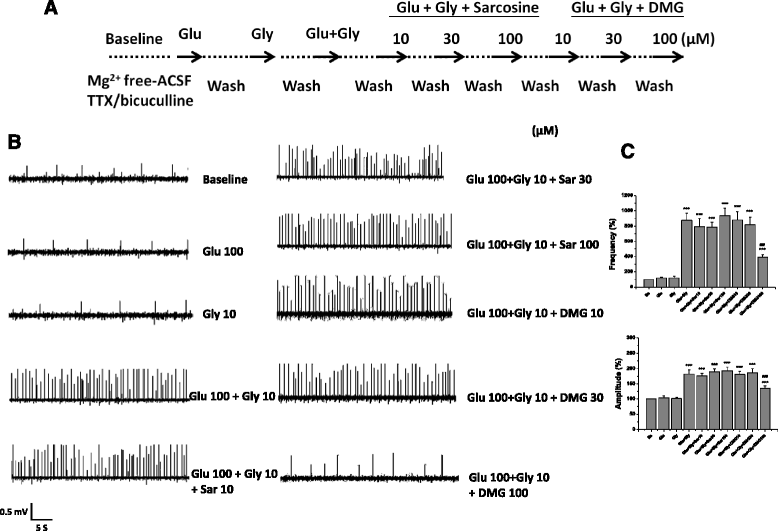
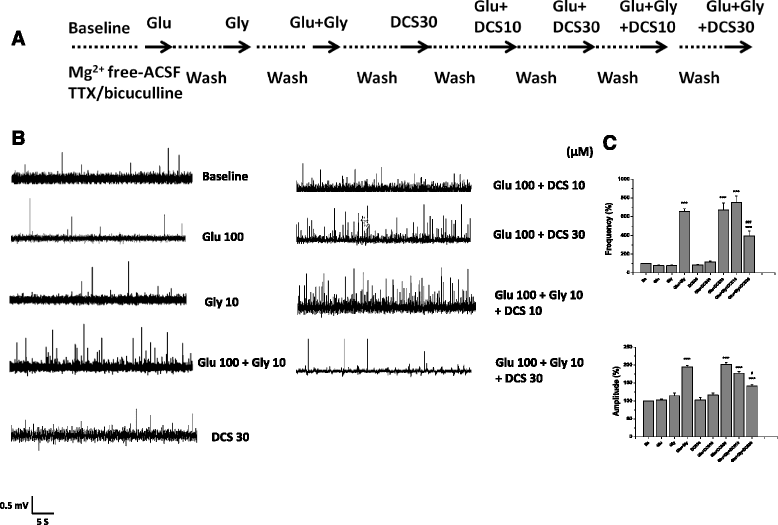
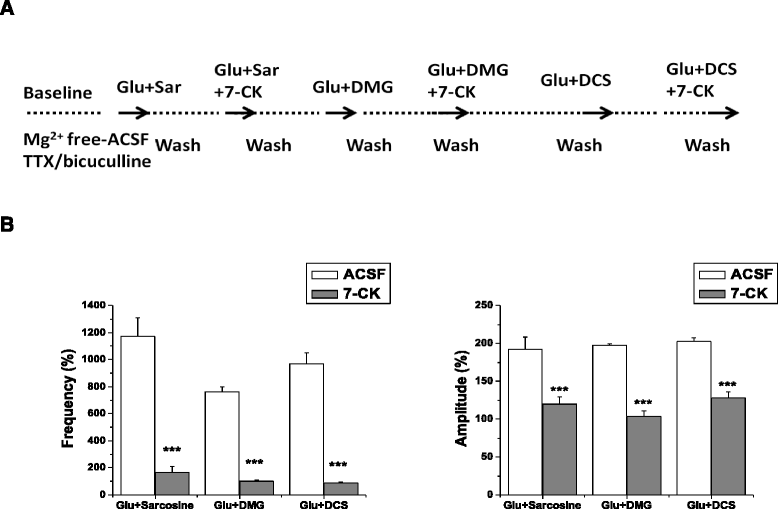
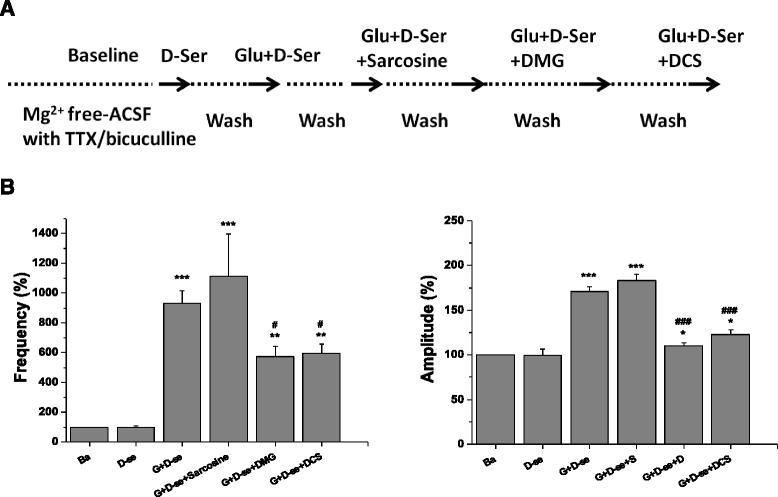
Results: Glycine, sarcosine and DMG alone did not alter the NMDA receptor-mediated EFPs, but in combination with glutamate, glycine and its N-methyl derivatives significantly increased the frequency and amplitude of EFPs. The enhancing effects of glycine analogs in combination with glutamate on EFPs were remarkably reduced by the glycine binding site antagonist 7-chlorokynurenate (7-CK). However, DMG, but not sarcosine, reduced the frequency and amplitude of EFPs elicited by co-application of glutamate plus glycine. D-cycloserine, a partial agonist at the glycine binding site on NMDA receptors, affected EFPs in a similar manner to DMG. Furthermore, DMG, but not sarcosine, reduced the frequencies and amplitudes of EFPs elicited by glutamate plus D-serine, another endogenous ligand for glycine binding site.
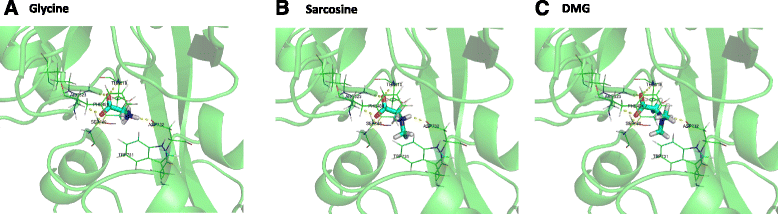
Conclusions: These findings suggest that sarcosine acts as a full agonist, yet DMG is a partial agonist at glycine binding site of NMDA receptors. The molecular docking analysis indicated that the interactions of glycine, sarcosine, and DMG to NMDA receptors are highly similar, supporting that the glycine binding site of NMDA receptors is a critical target site for sarcosine and DMG.
Keywords: 7-chlorokynurenate; D-cycloserine; D-serine; Glycine binding site; N-methylglycine.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Glycine tranporter-1 blockade potentiates NMDA-mediated responses in rat prefrontal cortical neurons in vitro and in vivo.J Neurophysiol. 2003 Feb;89(2):691-703. doi: 10.1152/jn.00680.2002. J Neurophysiol. 2003. PMID: 12574447
-
N,N-dimethylglycine differentially modulates psychotomimetic and antidepressant-like effects of ketamine in mice.Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016 Nov 3;71:7-13. doi: 10.1016/j.pnpbp.2016.06.002. Epub 2016 Jun 10. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27296677
-
The contribution of the NMDA receptor glycine site to rhythm generation during fictive swimming in Xenopus laevis tadpoles.Eur J Neurosci. 2007 Nov;26(9):2556-64. doi: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2007.05892.x. Epub 2007 Oct 23. Eur J Neurosci. 2007. PMID: 17970719
-
Glycine transporter-1: a new potential therapeutic target for schizophrenia.Curr Pharm Des. 2011;17(2):112-20. doi: 10.2174/138161211795049598. Curr Pharm Des. 2011. PMID: 21355838 Review.
-
Interactions between glycine transporter type 1 (GlyT-1) and some inhibitor molecules - glycine transporter type 1 and its inhibitors (review).Acta Physiol Hung. 2012 Mar;99(1):1-17. doi: 10.1556/APhysiol.99.2012.1.1. Acta Physiol Hung. 2012. PMID: 22425803 Review.
Cited by
-
Demystifying the Antidepressant Mechanism of Action of Stinels, a Novel Class of Neuroplastogens: Positive Allosteric Modulators of the NMDA Receptor.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025 Jan 24;18(2):157. doi: 10.3390/ph18020157. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40005971 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SMILE: systems metabolomics using interpretable learning and evolution.BMC Bioinformatics. 2021 May 28;22(1):284. doi: 10.1186/s12859-021-04209-1. BMC Bioinformatics. 2021. PMID: 34049495 Free PMC article.
-
Sarcosine sensitizes lung adenocarcinoma to chemotherapy by dual activation of ferroptosis via PDK4/PDHA1 signaling and NMDAR-mediated iron export.Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025 Apr 24;14(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s40164-025-00657-0. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2025. PMID: 40275333 Free PMC article.
-
Glycine Transporter 1 Inhibitors: Predictions on Their Possible Mechanisms in the Development of Opioid Analgesic Tolerance.Biomedicines. 2024 Feb 12;12(2):421. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12020421. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38398023 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxytocin-induced increase in N,N-dimethylglycine and time course of changes in oxytocin efficacy for autism social core symptoms.Mol Autism. 2021 Feb 23;12(1):15. doi: 10.1186/s13229-021-00423-z. Mol Autism. 2021. PMID: 33622389 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Burgdorf J, Zhang XL, Nicholson KL, Balster RL, Leander JD, Stanton PK, Gross AL, Kroes RA, Moskal JR. GLYX-13, a NMDA receptor glycine-site functional partial agonist, induces antidepressant-like effects without ketamine-like side effects. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2013;38(5):729–742. doi: 10.1038/npp.2012.246. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

