Californium-252 neutron brachytherapy combined with external pelvic radiotherapy plus concurrent chemotherapy for cervical cancer: a retrospective clinical study
- PMID: 28245859
- PMCID: PMC5331714
- DOI: 10.1186/s40880-017-0191-x
Californium-252 neutron brachytherapy combined with external pelvic radiotherapy plus concurrent chemotherapy for cervical cancer: a retrospective clinical study
Abstract
Background: Cervical cancer is the sixth most common cancer in Chinese women. A standard treatment modality for cervical cancer is the combination of surgery, chemotherapy, external-beam radiotherapy and intracavitary brachytherapy. The aim of this study was to retrospectively assess the long-term treatment outcomes of patients with cervical cancer who were treated with californium-252 neutron brachytherapy combined with external-beam radiotherapy plus concurrent chemotherapy.
Methods: We retrospectively analyzed the medical records of 150 patients with primary stages IB-IVB cervical cancer who received neutron brachytherapy combined with external-beam radiotherapy concurrently with cisplatin chemotherapy. All patients were followed up. Using an actuarial analysis, patient outcomes and treatment-related adverse effects were evaluated and compared.
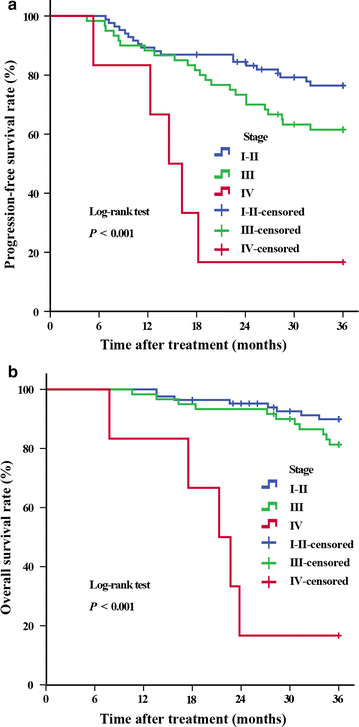
Results: The median overall survival (OS) was 33.2 months. The 3-year progression-free survival rates for patients with stages I-II, III, and IV diseases were 81.0% (68/84), 65.0% (39/60), and 0% (0/6), respectively; the 3-year OS rates were 90.5% (76/84), 85.0% (51/60), and 16.7% (1/6), respectively. Vaginal bleeding was controlled within the median time of 4.0 days. One month after treatment, 97.3% of patients achieved short-term local control. The local recurrence rates for patients with stages I-II, III, and IV disease were 4.8% (4/84), 11.7% (7/60), and 33.3% (2/6), respectively, and the occurrence rates of distant metastasis were 16.7% (14/84), 25.0% (15/60), and 100.0% (6/6), respectively. Cancer stage, tumor size, and lymph node metastasis were identified as prognostic risk factors, but only lymph node metastasis was found to be an independent prognostic factor. The most common adverse effects during treatment were grades 1 and 2 irradiation-related proctitis and radiocystitis.
Conclusion: For patients with cervical cancer, neutron brachytherapy combined with external-beam radiotherapy plus concurrent chemotherapy produces a rapid response and greatly improves local control and long-term survival rates with tolerable adverse effects.
Keywords: Californium-252; Cervical cancer; External-beam radiotherapy; Neutron brachytherapy.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Low-dose-rate californium-252 neutron intracavitary afterloading radiotherapy combined with conformal radiotherapy for treatment of cervical cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012 Jul 1;83(3):966-71. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2011.08.031. Epub 2011 Dec 3. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2012. PMID: 22138462
-
A feasibility study of 252Cf neutron brachytherapy, cisplatin + 5-FU chemo-adjuvant and accelerated hyperfractionated radiotherapy for advanced cervical cancer.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994 Jun 15;29(3):529-34. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(94)90450-2. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1994. PMID: 8005811 Clinical Trial.
-
Hypoxic versus normoxic external-beam irradiation of cervical carcinoma combined with californium-252 neutron brachytherapy. Comparative treatment results of a 5-year randomized study.Strahlenther Onkol. 2005 May;181(5):273-84. doi: 10.1007/s00066-005-1303-0. Strahlenther Onkol. 2005. PMID: 15900423 Clinical Trial.
-
Cervical cancer: combined modality therapy.Cancer J. 2001 Jul-Aug;7 Suppl 1:S47-50. Cancer J. 2001. PMID: 11504285 Review.
-
[Radiochemotherapy of uterine cervix cancers. Recent data].Cancer Radiother. 2000 Mar-Apr;4(2):140-6. doi: 10.1016/s1278-3218(00)88898-8. Cancer Radiother. 2000. PMID: 10812360 Review. French.
Cited by
-
Current Updates on Cancer-Causing Types of Human Papillomaviruses (HPVs) in East, Southeast, and South Asia.Cancers (Basel). 2021 May 30;13(11):2691. doi: 10.3390/cancers13112691. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34070706 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Construction and validation of an innovative prognostic nomogram for overall survival in cervical cancer patients with lung metastasis: an analysis utilizing the SEER database.Front Oncol. 2024 May 8;14:1397454. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1397454. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38779094 Free PMC article.
-
miR-122-5p modulates the radiosensitivity of cervical cancer cells by regulating cell division cycle 25A (CDC25A).FEBS Open Bio. 2019 Nov;9(11):1869-1879. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12730. Epub 2019 Sep 29. FEBS Open Bio. 2019. PMID: 31505105 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of nimotuzumab combined with chemoradiotherapy in the treatment of locally advanced cervical cancer.Ann Transl Med. 2022 Dec;10(24):1322. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-5739. Ann Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 36660627 Free PMC article.
-
Score for the Overall Survival Probability of Patients With First-Diagnosed Distantly Metastatic Cervical Cancer: A Novel Nomogram-Based Risk Assessment System.Front Oncol. 2019 Nov 5;9:1106. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2019.01106. eCollection 2019. Front Oncol. 2019. PMID: 31750238 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Viswanathan AN, Thomadsen B. American Brachytherapy Society Cervical Cancer Recommendations Committee; American Brachytherapy Society. American Brachytherapy Society consensus guidelines for locally advanced carcinoma of the cervix. Part I: general principles. Brachytherapy. 2012;11(1):33–46. doi: 10.1016/j.brachy.2011.07.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

