Acupuncture decreased the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with fibromyalgia in Taiwan: a nationwide matched cohort study
- PMID: 28245860
- PMCID: PMC5331677
- DOI: 10.1186/s13075-017-1239-7
Acupuncture decreased the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with fibromyalgia in Taiwan: a nationwide matched cohort study
Abstract
Background: The aim of this study was to understand whether acupuncture can decrease the risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) in patients with fibromyalgia.
Methods: Using data from the Taiwanese National Health Insurance Research Database, we performed a propensity score-matched cohort study to analyze patients with fibromyalgia diagnosed between 1 January 2000 and 31 December 2010. Patients who received acupuncture treatment, beginning with their initial date of fibromyalgia diagnosis and extending to 31 December 2010, were regarded as the acupuncture cohort. The no-acupuncture cohort comprised patients who never received acupuncture through 31 December 2010. A Cox regression model was used to adjust for age, sex, comorbidities, and drugs used. The HRs of the acupuncture and no-acupuncture cohorts were compared.
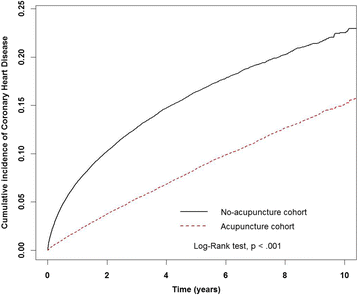
Results: After performing a 1:1 propensity score match, 58,899 patients in both cohorts were identified. Baseline characteristics were similar in both cohorts. The cumulative incidence of CHD was significantly lower in the acupuncture cohort (log-rank test, p < 0.001). In the follow-up period, 4389 patients in the acupuncture cohort (17.44 per 1000 person-years) and 8133 patients in the no-acupuncture cohort (38.36 per 1000 person-years) developed CHD (adjusted HR 0.43, 95% CI 0.41-0.45). The beneficial effect of acupuncture on the incidence of CHD was independent of age, sex, comorbidities, and statins used.
Conclusions: Our study confirmed that acupuncture reduced the risk of CHD in patients with fibromyalgia in Taiwan. Further clinical and mechanistic studies are warranted.
Keywords: Acupuncture; Coronary heart disease; Fibromyalgia; National Health Insurance Research Database; Taiwan.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Acupuncture decreased the risk of coronary heart disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis in Taiwan: a Nationwide propensity score-matched study.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018 Dec 22;18(1):341. doi: 10.1186/s12906-018-2384-5. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2018. PMID: 30577824 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture decreased the risk of stroke among patients with fibromyalgia in Taiwan: A nationwide matched cohort study.PLoS One. 2020 Oct 1;15(10):e0239703. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0239703. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 33002009 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Acupuncture treatment is associated with a decreased risk of developing stroke in patients with depression: A propensity-score matched cohort study.J Affect Disord. 2019 May 1;250:298-306. doi: 10.1016/j.jad.2019.03.020. Epub 2019 Mar 5. J Affect Disord. 2019. PMID: 30875672
-
A review of the incidence and risk factors for fibromyalgia and chronic widespread pain in population-based studies.Pain. 2020 Jun;161(6):1169-1176. doi: 10.1097/j.pain.0000000000001819. Pain. 2020. PMID: 32040078 Review.
-
Time to diagnosis of fibromyalgia and factors associated with delayed diagnosis in primary care.Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018 Aug;32(4):489-499. doi: 10.1016/j.berh.2019.01.019. Epub 2019 Mar 4. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2018. PMID: 31174818 Review.
Cited by
-
Knowledge Mapping of Acupuncture for Fibromyalgia from 1990 to 2022: A Bibliometric Analysis.J Pain Res. 2022 Aug 18;15:2405-2426. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S379699. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 36003289 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture Treatment is Associated with a Decreased Risk of Dementia in Patients with Depression: A Propensity Score-Matched Cohort Study.Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021 Nov 4;17:3255-3266. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S331026. eCollection 2021. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2021. PMID: 34764650 Free PMC article.
-
Long-Term Effect of Acupuncture on the Medical Expenditure and Risk of Depression and Anxiety in Migraine Patients: A Retrospective Cohort Study.Front Neurol. 2020 Apr 24;11:321. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2020.00321. eCollection 2020. Front Neurol. 2020. PMID: 32390934 Free PMC article.
-
Acupuncture therapy for fibromyalgia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.J Pain Res. 2019 Jan 30;12:527-542. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S186227. eCollection 2019. J Pain Res. 2019. PMID: 30787631 Free PMC article.
-
Trends in use of acupuncture among adults in Taiwan from 2002 to 2011: A nationwide population-based study.PLoS One. 2018 Apr 10;13(4):e0195490. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0195490. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 29634741 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Weir PT, Harlan GA, Nkoy FL, Jones SS, Hegmann KT, Gren LH, et al. The incidence of fibromyalgia and its associated comorbidities: a population-based retrospective cohort study based on International Classification of Diseases, 9th Revision codes. J Clin Rheumatol. 2006;12:124–8. doi: 10.1097/01.rhu.0000221817.46231.18. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

