Liver radiofrequency ablation as emergency treatment for a ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
- PMID: 28245861
- PMCID: PMC5331708
- DOI: 10.1186/s13256-017-1199-1
Liver radiofrequency ablation as emergency treatment for a ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma: a case report
Abstract
Background: Hemoperitoneum is a possible complication of hepatocellular carcinoma that may require emergency surgery as an alternative to radiological locoregional therapies.
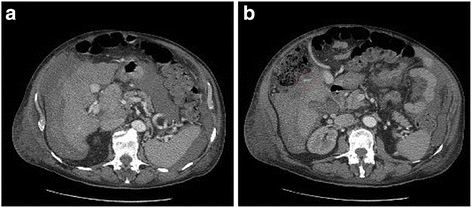
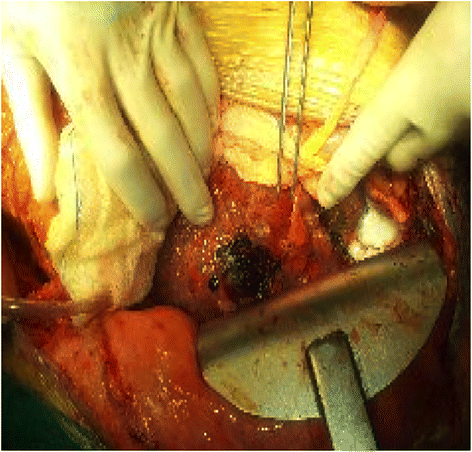
Case presentation: We present a case report of a 78-year-old white man with alcoholic-related cirrhosis and a multifocal hepatocellular carcinoma. An abdominal computed tomography scan showed multiple and bilateral foci of bleeding from broken liver cancer. He was urgently transferred from our radiology unit to our operating room for massive hemoperitoneum. A middle line laparotomy detected a massive hemoperitoneum. His liver was cirrhotic and completely subverted by a tumor; there were two spontaneous bleeding lacerations on segments II and IV, which were uncontrollable with conventional hemostatic techniques. Therefore, it was decided to carry out the coagulation of the multiple vascular afferents of each single mass by means of radiofrequency ablation cycles performed circumferentially on both nodules for a total of 40 minutes. Hemostasis was achieved; the radiofrequency ablation controlled the bleeding from his ruptured hepatocellular carcinoma. He was transferred to our intensive care unit for postoperative monitoring in terms of hemodynamic stability. On postoperative day 2 he was discharged from our intensive care unit.
Conclusions: Multifocal bleeding hepatocellular carcinoma still has an extremely high mortality. The angiographic control of multiple bilateral bleeding lesions can be extremely difficult and can be contraindicated by the location of the lesions and by the overall clinical condition of the patient. In this case, treatment with radiofrequency ablation has proven to be effective in the control of multiple and bilateral hepatic lesions. This particular technique allowed us to attack the lesion at the level of the vascular pedicle in order to control the bleeding.
Keywords: Case report; HCC ruptured; Liver bleeding; Radiofrequency ablation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Management of spontaneous bleeding due to hepatocellular carcinoma.Minerva Chir. 2002 Jun;57(3):347-56. Minerva Chir. 2002. PMID: 12029230 English, Italian.
-
Hemoperitoneum as a first manifestation of hepatocellular carcinoma in western patients with liver cirrhosis: effectiveness of emergency treatment with transcatheter arterial embolization.Dig Dis Sci. 2001 Mar;46(3):555-62. doi: 10.1023/a:1005699132142. Dig Dis Sci. 2001. PMID: 11318532
-
Hemoperitoneum as a first manifestation of HCC with bleeding from ruptured aberrant vessel: a case report.Trop Gastroenterol. 2006 Jan-Mar;27(1):48-9. Trop Gastroenterol. 2006. PMID: 16910063
-
Surgical treatment in a patient with multiple implanted intraperitoneal metastases after resection of ruptured large hepatocellular carcinoma.Hepatogastroenterology. 2004 Jan-Feb;51(55):239-42. Hepatogastroenterology. 2004. PMID: 15011873 Review.
-
Acute hemoperitoneum from rupture of a hepatocellular carcinoma.J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988 Apr;10(2):221-5. doi: 10.1097/00004836-198804000-00025. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1988. PMID: 2843591 Review.
Cited by
-
One-lung ventilation to treat hepatic dome lesion - a further step towards minimally invasive surgery: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2019 Mar 24;13(1):83. doi: 10.1186/s13256-019-1999-6. J Med Case Rep. 2019. PMID: 30904019 Free PMC article.
-
Colorectal Liver Metastases: A Literature Review of Viable Surgical Options with a Special Focus on Microwave Liver Thermal Ablation and Mini-Invasive Approach.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 23;13(1):33. doi: 10.3390/jpm13010033. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36675694 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ruptured Hepatocellular Carcinoma: What Do Interventional Radiologists Need to Know?Front Oncol. 2022 Jun 16;12:927123. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.927123. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35785181 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pulsed Microwave Liver Ablation: An Additional Tool to Treat Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 31;14(3):748. doi: 10.3390/cancers14030748. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35159014 Free PMC article.
-
Hemostasis using re-radiofrequency ablation for hepatic tract bleeding after ultrasound-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic tumors.Br J Radiol. 2021 Dec;94(1128):20210353. doi: 10.1259/bjr.20210353. Epub 2021 Sep 19. Br J Radiol. 2021. PMID: 34538063 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miyamoto M, Sudo T, Kuyama T. Spontaneous rupture of hepatocellular carcinoma: a review of 172 Japanese cases. Am J Gastroenterol. 1991;86:67–71. - PubMed
-
- Chearanai O, Plengvanit U, Asavanich C, Damrongsak D, Sindhvananda K, Boonyapisit S. Spontaneous rupture of primary hepatoma: report of 63 cases with particular reference to the pathogenesis and rationale treatment by hepatic artery ligation. Cancer. 1983;51:1532–1536. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19830415)51:8<1532::AID-CNCR2820510829>3.0.CO;2-3. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical