Effect of two lipid-lowering strategies on high-density lipoprotein function and some HDL-related proteins: a randomized clinical trial
- PMID: 28245873
- PMCID: PMC5331745
- DOI: 10.1186/s12944-017-0433-6
Effect of two lipid-lowering strategies on high-density lipoprotein function and some HDL-related proteins: a randomized clinical trial
Abstract
Background: The influence of lipid-lowering therapy on high-density lipoprotein (HDL) is incompletely understood. We compared the effect of two lipid-lowering strategies on HDL functions and identified some HDL-related proteins.
Methods: Thirty two patients were initially screened and HDLs of 21 patients were finally analyzed. Patients were randomized to receive atorvastatin 20 mg (n = 11) or atorvastatin 5 mg/ezetimibe 10 mg combination (n = 10) for 8 weeks. The cholesterol efflux capacity and other anti-inflammatory functions were assessed based on HDLs of the participants before and after treatment. Pre-specified HDL proteins of the same HDL samples were measured.
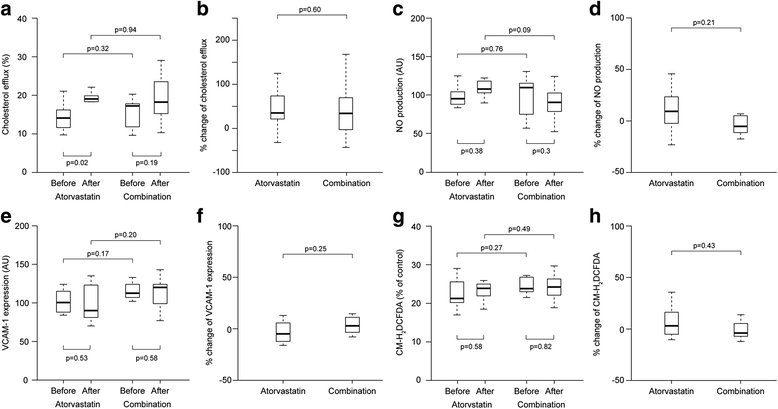
Results: The post-treatment increase in cholesterol efflux capacities was similar between the groups (35.6% and 34.6% for mono-therapy and combination, respectively, p = 0.60). Changes in nitric oxide (NO) production, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (VCAM-1) expression, and reactive oxygen species (ROS) production were similar between the groups. The baseline cholesterol efflux capacity correlated positively with apolipoprotein (apo)A1 and C3, whereas apoA1 and apoC1 showed inverse associations with VCAM-1 expression. The changes in the cholesterol efflux capacity were positively correlated with multiple HDL proteins, especially apoA2.
Conclusions: Two regimens increased the cholesterol efflux capacity of HDL comparably. Multiple HDL proteins, not limited to apoA1, showed a correlation with HDL functions. These results indicate that conventional lipid therapy may have additional effects on HDL functions with changes in HDL proteins.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov, number NCT02942602 .
Keywords: Atorvastatin calcium; Cholesterol-efflux regulatory protein; Ezetimibe; Inflammation.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Achievement of specified low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol apolipoprotein B, and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein levels with ezetimibe/simvastatin or atorvastatin in metabolic syndrome patients with and without atherosclerotic vascular disease (from the VYMET study).J Clin Lipidol. 2011 Nov-Dec;5(6):474-82. doi: 10.1016/j.jacl.2011.06.004. Epub 2011 Jun 15. J Clin Lipidol. 2011. PMID: 22108151 Clinical Trial.
-
Lipid-altering efficacy and safety of ezetimibe/simvastatin versus atorvastatin in patients with hypercholesterolemia and the metabolic syndrome (from the VYMET study).Am J Cardiol. 2009 Jun 15;103(12):1694-702. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2009.05.003. Am J Cardiol. 2009. PMID: 19539078 Clinical Trial.
-
Effects of rosuvastatin versus atorvastatin, simvastatin, and pravastatin on non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol, apolipoproteins, and lipid ratios in patients with hypercholesterolemia: additional results from the STELLAR trial.Clin Ther. 2004 Sep;26(9):1388-99. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2004.09.006. Clin Ther. 2004. PMID: 15531001 Clinical Trial.
-
Comparing the combination therapy of ezetimibe and atorvastatin with atorvastatin monotherapy for regulating blood lipids: a systematic review and meta-analyse.Lipids Health Dis. 2018 Oct 17;17(1):239. doi: 10.1186/s12944-018-0880-8. Lipids Health Dis. 2018. PMID: 30326894 Free PMC article.
-
Pitavastatin: novel effects on lipid parameters.Atheroscler Suppl. 2011 Nov;12(3):277-84. doi: 10.1016/S1567-5688(11)70887-X. Atheroscler Suppl. 2011. PMID: 22152282 Review.
Cited by
-
Hypercholesterolemia-Induced HDL Dysfunction Can Be Reversed: The Impact of Diet and Statin Treatment in a Preclinical Animal Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 2;23(15):8596. doi: 10.3390/ijms23158596. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35955730 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Therapeutic Agents That Target ATP Binding Cassette A1 (ABCA1) Gene Expression.Drugs. 2022 Jul;82(10):1055-1075. doi: 10.1007/s40265-022-01743-x. Epub 2022 Jul 21. Drugs. 2022. PMID: 35861923 Review.
-
Ezetimibe Monotherapy Reduces Serum Levels of Platelet-Activating Factor Acetylhydrolase in Patients With Dyslipidemia.J Clin Med Res. 2019 Oct;11(10):676-681. doi: 10.14740/jocmr3901. Epub 2019 Oct 4. J Clin Med Res. 2019. PMID: 31636781 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Reiner Z, Catapano AL, De Backer G, Graham I, Taskinen MR, Wiklund O, et al. ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: the Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS) Eur Heart J. 2011;32:1769–1818. doi: 10.1093/eurheartj/ehr158. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Stone NJ, Robinson JG, Lichtenstein AH, Bairey Merz CN, Blum CB, Eckel RH, et al. 2013 ACC/AHA guideline on the treatment of blood cholesterol to reduce atherosclerotic cardiovascular risk in adults: a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. Circulation. 2014;129:S1–S45. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.0000437738.63853.7a. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

