Timing of thoracic radiotherapy in the treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: important or not?
- PMID: 28245874
- PMCID: PMC5331725
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-017-0779-y
Timing of thoracic radiotherapy in the treatment of extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer: important or not?
Abstract
Background: This study evaluated the prognosis of patients with extensive-stage small-cell lung cancer (ES-SCLC) that may be associated with timing of thoracic radiotherapy (TRT).
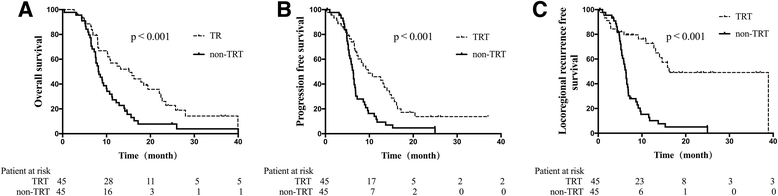
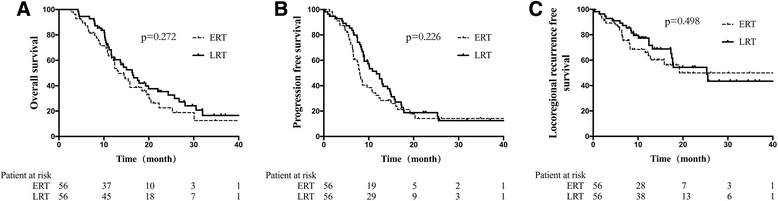
Methods: ES-SCLC patients (n = 232) without progression were retrospectively analyzed after first-line induction chemotherapy. Patients in the TRT group were stratified as early-TRT (ERT; ≤3 cycles of induction chemotherapy received prior to TRT, n = 65) or late-TRT (LRT; >3 cycles, n = 122). To avoid selection bias, we conducted Propensity Score Matching (PSM) for patients. Overall survival (OS), progression-free survival (PFS), and locoregional recurrence-free survival (LRRFS) were assessed and compared.
Results: Overall, the median survival time, PFS, and LRRFS were 13.2, 8.7, and 14.6 months, respectively. After matching by PSM, there were 45 patients total in the TRT/non-TRT groups, and 56 patients total in the ERT/LRT groups. OS, PFS, and LRRFS were significantly longer in the TRT group than the non-TRT group (P < 0.001, all). However, between the ERT and LRT groups these survival parameters were similar (P > 0.05, all).
Conclusion: For ES-SCLC patients without progression, the addition of TRT after first-line chemotherapy benefited survival greatly. Early TRT showed no significant benefit over late TRT.
Keywords: Early/late radiotherapy; Prognosis; Radiotherapy; Small cell lung cancer.
Figures
References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

