Targeting TGF-β Signaling for Therapeutic Gain
- PMID: 28246179
- PMCID: PMC5630004
- DOI: 10.1101/cshperspect.a022301
Targeting TGF-β Signaling for Therapeutic Gain
Abstract
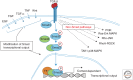
Transforming growth factor βs (TGF-βs) are closely related ligands that have pleiotropic activity on most cell types of the body. They act through common heterotetrameric TGF-β type II and type I transmembrane dual specificity kinase receptor complexes, and the outcome of signaling is context-dependent. In normal tissue, they serve a role in maintaining homeostasis. In many diseased states, particularly fibrosis and cancer, TGF-β ligands are overexpressed and the outcome of signaling is diverted toward disease progression. There has therefore been a concerted effort to develop drugs that block TGF-β signaling for therapeutic benefit. This review will cover the basics of TGF-β signaling and its biological activities relevant to oncology, present a summary of pharmacological TGF-β blockade strategies, and give an update on preclinical and clinical trials for TGF-β blockade in a variety of solid tumor types.
Copyright © 2017 Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; all rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Akhurst RJ. 2004. TGF-β signaling in health and disease. Nat Genet 36: 790–792. - PubMed
-
- Akhurst RJ, Derynck R. 2001. TGF-β signaling in cancer—A double-edged sword. Trends Cell Biol 11: S44–51. - PubMed
-
- Akhurst RJ, Fee F, Balmain A. 1988. Localized production of TGF-β mRNA in tumour promoter-stimulated mouse epidermis. Nature 331: 363–365. - PubMed
-
- Anderton MJ, Mellor HR, Bell A, Sadler C, Pass M, Powell S, Steele SJ, Roberts RR, Heier A. 2011. Induction of heart valve lesions by small-molecule ALK5 inhibitors. Toxicol Pathol 39: 916–924. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
