Decreased Tissue COX5B Expression and Mitochondrial Dysfunction during Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury in Rats
- PMID: 28246552
- PMCID: PMC5299166
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/8498510
Decreased Tissue COX5B Expression and Mitochondrial Dysfunction during Sepsis-Induced Kidney Injury in Rats
Abstract
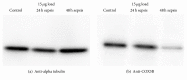
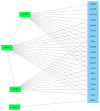
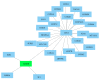
Background. Sepsis is defined as a life-threatening organ dysfunction due to a dysregulated host response to infection. Sepsis is the dominant cause of acute kidney injury (AKI), accounting for nearly 50% of episodes of acute renal failure. Signaling cascades and pathways within the kidney are largely unknown and analysis of these molecular mechanisms may enhance knowledge on pathophysiology and possible therapeutic options. Material and Methods. 26 male Wistar rats were assigned to either a sham group (control, N = 6) or sepsis group (N = 20; cecal ligature and puncture model, 24 and 48 hours after CLP). Surviving rats (n = 12) were decapitated at 24 hours (early phase; n = 6) or 48 hours (late phase; n = 6) after CLP and kidneys removed for proteomic analysis. 2D-DIGE and DeCyder 2D software (t-test, P < 0.01) were used for analysis of significantly regulated protein spots. MALDI-TOF in combination with peptide mass fingerprinting (PMF) as well as Western Blot analysis was used for protein identification. Bioinformatic network analyses (STRING, GeneMania, and PCViz) were used to describe protein-protein interactions. Results. 12 spots were identified with significantly altered proteins (P < 0.01) in the three analyzed groups. Two spots could not be identified. Four different proteins were found significantly changed among the groups: major urinary protein (MUP5), cytochrome c oxidase subunit B (COX5b), myosin-6 (MYH6), and myosin-7 (MYH7). A significant correlation with the proteins was found for mitochondrial energy production and electron transport. Conclusions. COX5B could be a promising biomarker candidate since a significant association was found during experimental sepsis in the present study. For future research, COX5B should be evaluated as a biomarker in both human urine and serum to identify sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interests.
Figures



References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

