A Retrospective Video Analysis of Canonical Babbling and Volubility in Infants with Fragile X Syndrome at 9-12 Months of Age
- PMID: 28247019
- PMCID: PMC5450668
- DOI: 10.1007/s10803-017-3033-4
A Retrospective Video Analysis of Canonical Babbling and Volubility in Infants with Fragile X Syndrome at 9-12 Months of Age
Abstract
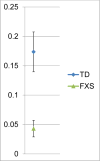
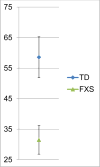
An infant's vocal capacity develops significantly during the first year of life. Research suggests early measures of pre-speech development, such as canonical babbling and volubility, can differentiate typical versus disordered development. This study offers a new contribution by comparing early vocal development in 10 infants with Fragile X syndrome and 14 with typical development. Results suggest infants with Fragile X syndrome produce fewer syllables and have significantly lower canonical babbling ratios compared to infants who are typically developing. Furthermore, the particular measures of babbling were strong predictors of group membership, adding evidence regarding the possible utility of these markers in early identification.
Keywords: Canonical babbling; Fragile X syndrome; Language development.
Figures
References
-
- Abbeduto L, Hagerman RJ. Language and communication in fragile X syndrome. Mental Retardation and Developmental Disabilities Research Reviews. 1997;3(4):313–322.
-
- Abbeduto L, Murphy MM, Cawthon SW, Richmond EK, Weissman MD, Karadottir S, O’Brien A. Receptive language skills of adolescents and young adults with Down or fragile X syndrome. American Journal on Mental Retardation. 2003;108(3):149–160. - PubMed
-
- Bailey DB, Jr, Hatton DD, Skinner M. Early developmental trajectories of males with fragile X syndrome. American Journal on Mental Retardation. 1998;103(1):29–39. - PubMed
-
- Bailey DB, Raspa M, Bishop E, Holiday D. No change in the age of diagnosis for fragile X syndrome: Findings from a national parent survey. Pediatrics. 2009;124(2):527–533. - PubMed
-
- Baranek GT. Autism during infancy: A retrospective video analysis of sensory-motor and social behaviors at 9–12 months of age. Journal of Autism and Developmental Disorders. 1999;29(3):213–224. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical