Targeting noncoding RNAs in disease
- PMID: 28248199
- PMCID: PMC5330746
- DOI: 10.1172/JCI84424
Targeting noncoding RNAs in disease
Abstract
Many RNA species have been identified as important players in the development of chronic diseases, including cancer. Over the past decade, numerous studies have highlighted how regulatory RNAs such as microRNAs (miRNAs) and long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) play crucial roles in the development of a disease state. It is clear that the aberrant expression of miRNAs promotes tumor initiation and progression, is linked with cardiac dysfunction, allows for the improper physiological response in maintaining glucose and insulin levels, and can prevent the appropriate integration of neuronal networks, resulting in neurodegenerative disorders. Because of this, there has been a major effort to therapeutically target these noncoding RNAs. In just the past 5 years, over 100 antisense oligonucleotide-based therapies have been tested in phase I clinical trials, a quarter of which have reached phase II/III. Most notable are fomivirsen and mipomersen, which have received FDA approval to treat cytomegalovirus retinitis and high blood cholesterol, respectively. The continued improvement of innovative RNA modifications and delivery entities, such as nanoparticles, will aid in the development of future RNA-based therapeutics for a broader range of chronic diseases. Here we summarize the latest promises and challenges of targeting noncoding RNAs in disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
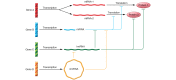
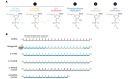

References
-
- Mattick JS, Makunin Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet. 2006;15(suppl 1):R17–R29. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

