The Diacetyl-Exposed Human Airway Epithelial Secretome: New Insights into Flavoring-Induced Airways Disease
- PMID: 28248570
- PMCID: PMC5516294
- DOI: 10.1165/rcmb.2016-0372OC
The Diacetyl-Exposed Human Airway Epithelial Secretome: New Insights into Flavoring-Induced Airways Disease
Abstract
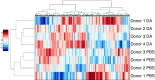
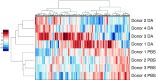
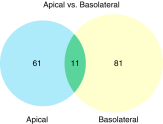
Bronchiolitis obliterans (BO) is an increasingly important lung disease characterized by fibroproliferative airway lesions and decrements in lung function. Occupational exposure to the artificial food flavoring ingredient diacetyl, commonly used to impart a buttery flavor to microwave popcorn, has been associated with BO development. In the occupational setting, diacetyl vapor is first encountered by the airway epithelium. To better understand the effects of diacetyl vapor on the airway epithelium, we used an unbiased proteomic approach to characterize both the apical and basolateral secretomes of air-liquid interface cultures of primary human airway epithelial cells from four unique donors after exposure to an occupationally relevant concentration (∼1,100 ppm) of diacetyl vapor or phosphate-buffered saline as a control on alternating days. Basolateral and apical supernatants collected 48 h after the third exposure were analyzed using one-dimensional liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. Paired t tests adjusted for multiple comparisons were used to assess differential expression between diacetyl and phosphate-buffered saline exposure. Of the significantly differentially expressed proteins identified, 61 were unique to the apical secretome, 81 were unique to the basolateral secretome, and 11 were present in both. Pathway enrichment analysis using publicly available databases revealed that proteins associated with matrix remodeling, including degradation, assembly, and new matrix organization, were overrepresented in the data sets. Similarly, protein modifiers of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling were significantly altered. The ordered changes in protein expression suggest that the airway epithelial response to diacetyl may contribute to BO pathogenesis.
Keywords: 2,3-butanedione; bronchiolitis obliterans; diacetyl; occupational lung disease; proteomics.
Figures
References
-
- Kreiss K, Gomaa A, Kullman G, Fedan K, Simoes EJ, Enright PL. Clinical bronchiolitis obliterans in workers at a microwave-popcorn plant. N Engl J Med. 2002;347:330–338. - PubMed
-
- Lockey JE, Hilbert TJ, Levin LP, Ryan PH, White KL, Borton EK, Rice CH, McKay RT, LeMasters GK. Airway obstruction related to diacetyl exposure at microwave popcorn production facilities. Eur Respir J. 2009;34:63–71. - PubMed
-
- Akpinar-Elci M, Travis WD, Lynch DA, Kreiss K. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome in popcorn production plant workers. Eur Respir J. 2004;24:298–302. - PubMed
-
- Kim TJ, Materna BL, Prudhomme JC, Fedan KB, Enright PL, Sahakian NM, Windham GC, Kreiss K. Industry-wide medical surveillance of California flavor manufacturing workers: cross-sectional results. Am J Ind Med. 2010;53:857–865. - PubMed
-
- van Rooy FG, Rooyackers JM, Prokop M, Houba R, Smit LA, Heederik DJ. Bronchiolitis obliterans syndrome in chemical workers producing diacetyl for food flavorings. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2007;176:498–504. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

