A three-long noncoding RNA signature as a diagnostic biomarker for differentiating between triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancers
- PMID: 28248879
- PMCID: PMC5340452
- DOI: 10.1097/MD.0000000000006222
A three-long noncoding RNA signature as a diagnostic biomarker for differentiating between triple-negative and non-triple-negative breast cancers
Abstract
Background: Triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) is an aggressive cancer with unfavorable outcome and it is useful to explore noninvasive biomarkers for its early diagnosis. Here, we identified differentially expressed long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) in blood samples of patients with TNBC to assess their diagnostic value.
Methods: Differential expression of lncRNAs in plasma of patients with TNBC (n = 25) and non-TNBC (NTNBC; n = 35) and in healthy controls was compared by microarray analysis and validated by real-time PCR. lncRNA expression between plasma and BC tissues was compared using Pearson correlation test. Logit model was used to obtain a new lncRNA-based score. Receiver operating characteristic analysis was performed to assess the diagnostic value of the selected lncRNAs.
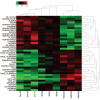
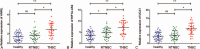
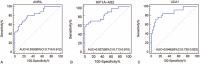
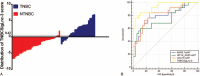
Results: Microarray data showed that 41 lncRNAs were aberrantly expressed. Among these, antisense noncoding RNA in the INK4 locus (ANRIL), hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha antisense RNA-2 (HIF1A-AS2), and urothelial carcinoma-associated 1 (UCA1) were markedly upregulated in plasma of patients with TNBC compared with patients with NTNBC (P < 0.01). HIF1A-AS2 expression was positively associated with its tissue levels (r = 0.670, P < 0.01). AUC (95% CI) of ANRIL, HIF1A-AS2, and UCA1 was 0.785 (0.660-0.881), 0.739 (0.610-0.844), and 0.817 (0.696-0.905), respectively. TNBCSigLnc-3, a new score obtained using the logit model, showed excellent diagnostic performance, with AUC of 0.934 (0.839-0.982), sensitivity of 76.0%, and specificity of 97.1%.
Conclusion: ANRIL, HIF1A-AS2, and UCA1 expression was significantly increased in plasma of patients with TNBC, suggesting their use as TNBC-specific diagnostic biomarkers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Figures



References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2015. CA Cancer J Clin 2015;65:5–29. - PubMed
-
- Foulkes WD, Smith IE, Reis-Filho JS. Triple-negative breast cancer. N Engl J Med 2010;363:1938–48. - PubMed
-
- Yin WJ, Lu JS, Di GH, et al. Clinicopathological features of the triple-negative tumors in Chinese breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009;115:325–33. - PubMed
-
- Basso SM, Santeufemia DA, Fadda GM, et al. Advances in the treatment of triple-negative early breast cancer. Med Chem 2016;12:268–72. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

