A genome-wide analysis of the lysophosphatidate acyltransferase (LPAAT) gene family in cotton: organization, expression, sequence variation, and association with seed oil content and fiber quality
- PMID: 28249560
- PMCID: PMC5333453
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-017-3594-9
A genome-wide analysis of the lysophosphatidate acyltransferase (LPAAT) gene family in cotton: organization, expression, sequence variation, and association with seed oil content and fiber quality
Abstract
Background: Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAAT) encoded by a multigene family is a rate-limiting enzyme in the Kennedy pathway in higher plants. Cotton is the most important natural fiber crop and one of the most important oilseed crops. However, little is known on genes coding for LPAATs involved in oil biosynthesis with regard to its genome organization, diversity, expression, natural genetic variation, and association with fiber development and oil content in cotton.
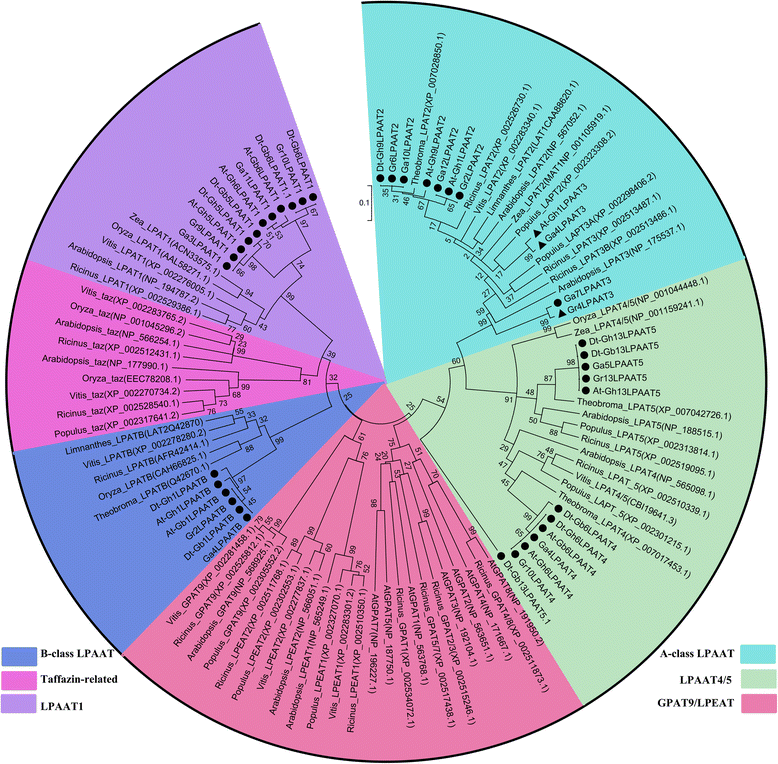
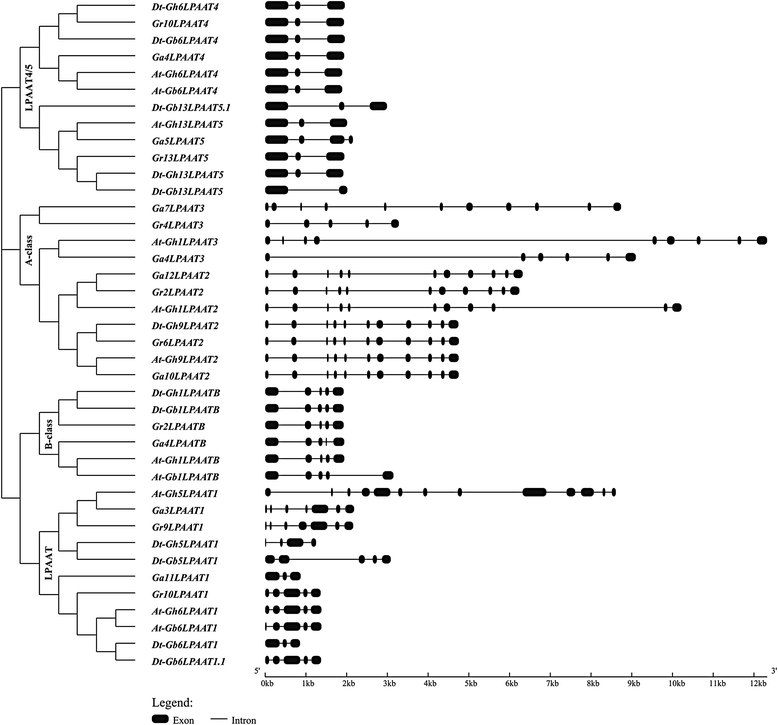
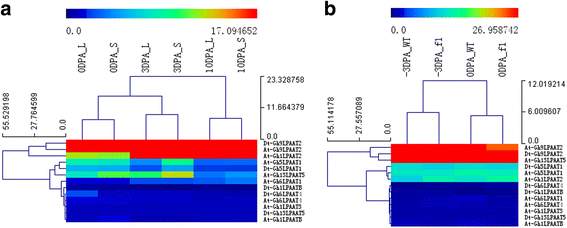
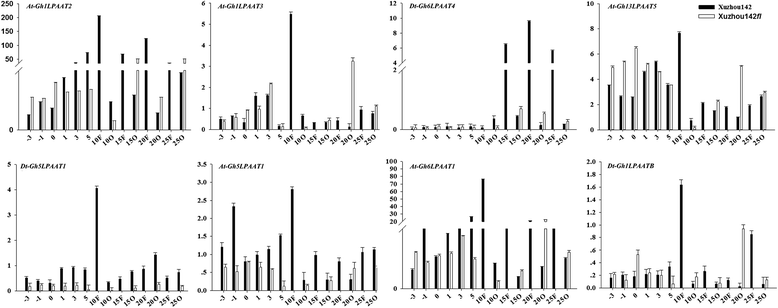
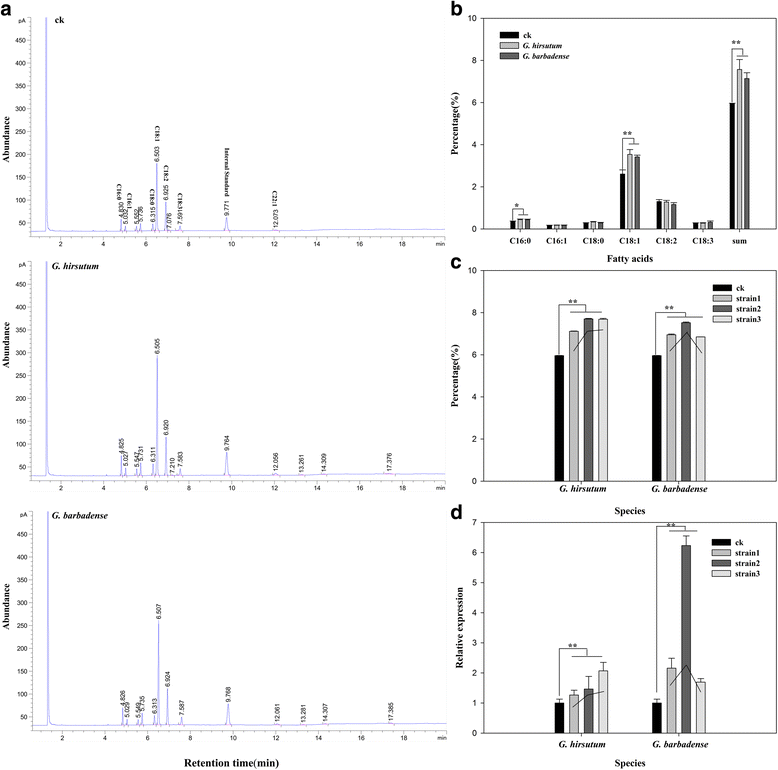
Results: In this study, a comprehensive genome-wide analysis in four Gossypium species with genome sequences, i.e., tetraploid G. hirsutum- AD1 and G. barbadense- AD2 and its possible ancestral diploids G. raimondii- D5 and G. arboreum- A2, identified 13, 10, 8, and 9 LPAAT genes, respectively, that were divided into four subfamilies. RNA-seq analyses of the LPAAT genes in the widely grown G. hirsutum suggest their differential expression at the transcriptional level in developing cottonseeds and fibers. Although 10 LPAAT genes were co-localised with quantitative trait loci (QTL) for cottonseed oil or protein content within a 25-cM region, only one single strand conformation polymorphic (SSCP) marker developed from a synonymous single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) of the At-Gh13LPAAT5 gene was significantly correlated with cottonseed oil and protein contents in one of the three field tests. Moreover, transformed yeasts using the At-Gh13LPAAT5 gene with the two sequences for the SNP led to similar results, i.e., a 25-31% increase in palmitic acid and oleic acid, and a 16-29% increase in total triacylglycerol (TAG).
Conclusions: The results in this study demonstrated that the natural variation in the LPAAT genes to improving cottonseed oil content and fiber quality is limited; therefore, traditional cross breeding should not expect much progress in improving cottonseed oil content or fiber quality through a marker-assisted selection for the LPAAT genes. However, enhancing the expression of one of the LPAAT genes such as At-Gh13LPAAT5 can significantly increase the production of total TAG and other fatty acids, providing an incentive for further studies into the use of LPAAT genes to increase cottonseed oil content through biotechnology.
Keywords: Gene expression patterns; Gossypium spp; Lysophosphatidic acid acyltransferase (LPAAT); Seed oil; Sequence variation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A genome-wide analysis of the phospholipid: diacylglycerol acyltransferase gene family in Gossypium.BMC Genomics. 2019 May 22;20(1):402. doi: 10.1186/s12864-019-5728-8. BMC Genomics. 2019. PMID: 31117950 Free PMC article.
-
[Genome-wide analysis of the LPAAT gene family in Gossypium raimondii and G. arboreum, and expression analysis of its orthologs in G. hirsutum].Yi Chuan. 2015 Jul;37(7):692-701. doi: 10.16288/j.yczz.15-010. Yi Chuan. 2015. PMID: 26351169 Chinese.
-
Identification of candidate genes from the SAD gene family in cotton for determination of cottonseed oil composition.Mol Genet Genomics. 2017 Feb;292(1):173-186. doi: 10.1007/s00438-016-1265-1. Epub 2016 Oct 28. Mol Genet Genomics. 2017. PMID: 27796643
-
Genetics, Breeding and Genetic Engineering to Improve Cottonseed Oil and Protein: A Review.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Mar 10;13:864850. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.864850. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35360295 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic and co-expression network analyses reveal candidate genes for oil accumulation based on an introgression population in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum).Theor Appl Genet. 2024 Jan 17;137(1):23. doi: 10.1007/s00122-023-04527-3. Theor Appl Genet. 2024. PMID: 38231256 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and analysis of oil candidate genes reveals the molecular basis of cottonseed oil accumulation in Gossypium hirsutum L.Theor Appl Genet. 2022 Feb;135(2):449-460. doi: 10.1007/s00122-021-03975-z. Epub 2021 Oct 29. Theor Appl Genet. 2022. PMID: 34714356
-
Effect of Heterologous Expression of Key Enzymes Involved in Astaxanthin and Lipid Synthesis on Lipid and Carotenoid Production in Aurantiochytrium sp.Mar Drugs. 2025 Apr 11;23(4):164. doi: 10.3390/md23040164. Mar Drugs. 2025. PMID: 40278285 Free PMC article.
-
Hub Genes in Stable QTLs Orchestrate the Accumulation of Cottonseed Oil in Upland Cotton via Catalyzing Key Steps of Lipid-Related Pathways.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Nov 22;24(23):16595. doi: 10.3390/ijms242316595. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 38068920 Free PMC article.
-
Increase in lysophosphatidate acyltransferase activity in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) increases seed triacylglycerol content despite its low intrinsic flux control coefficient.New Phytol. 2019 Oct;224(2):700-711. doi: 10.1111/nph.16100. Epub 2019 Sep 14. New Phytol. 2019. PMID: 31400160 Free PMC article.
-
Linkage and association analyses reveal that hub genes in energy-flow and lipid biosynthesis pathways form a cluster in upland cotton.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022 Apr 15;20:1841-1859. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2022.04.012. eCollection 2022. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2022. PMID: 35521543 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Liu Q, Singh S, Chapman K, Green A. Bridging traditional and molecular genetics in modifying cottonseed oil. Genet Genomics Cotton. 2009;3:353–83. doi: 10.1007/978-0-387-70810-2_15. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

