Do selective radiation dose escalation and tumour hypoxia status impact the loco-regional tumour control after radio-chemotherapy of head & neck tumours? The ESCALOX protocol
- PMID: 28249612
- PMCID: PMC5333380
- DOI: 10.1186/s13014-017-0776-1
Do selective radiation dose escalation and tumour hypoxia status impact the loco-regional tumour control after radio-chemotherapy of head & neck tumours? The ESCALOX protocol
Abstract
Background: Standard of care primary treatment of carcinoma of locally advanced squamous cell head and neck cancer (LAHNSCC) consists of platinum-based concomitant chemo-irradiation. Despite progress in the treatment of LAHNSCC using modern radiotherapy techniques the outcome remains still poor. Using IMRT with SIB the escalation of total dose to the GTV is possible with the aim to improve clinical outcome. This study tests the hypothesis if radiation dose escalation to the GTV improves 2-year-LRC and -OS after concomitant chemo-irradiation.
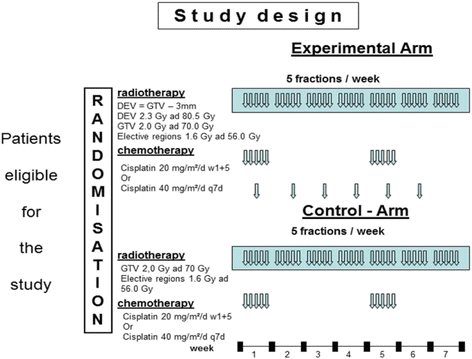
Methods: The ESCALOX trial is a prospective randomized phase III study using cisplatin chemo-irradiation and the SIB-IMRT concept in patients with LAHNSCC of the oral cavity, oropharynx or hypopharynx to escalate the total dose to the GTV up to 80.5 Gy. Chemotherapy is planned either in the 1st and 5th week (cisplatin 20 mg/m2/d d 1-5 and d 29-33) or weekly (cisplatin 40 mg/m2/d) during RT. RT is delivered as SIB with total doses of 80.5 Gy/70.0 Gy/56.0 Gy with 2.3 Gy/2.0 Gy and 1.6 Gy in the experimental arm and in the control arm with 70.0 Gy/56.0 Gy with 2.0 Gy and 1.6 Gy. A pre-study with dose escalation up to 77.0 Gy/70.0 Gy/56.0 Gy with 2.2 Gy/2.0 Gy and 1.6 Gy is demanded by the German federal office of radiation protection (BfS). In the translational part of the trial 100 of the randomised patients will be investigated by 18-F-FMiso-PET-CT for the presence and behaviour of tumor hypoxia twice in the week before treatment start.
Discussion: The primary endpoint of the pre-study is acute radiation induced toxicity. Primary endpoint of the main trial is 2-year-LRC. By using the dose escalation up to 80.5 Gy to the GTV of the primary tumor and lymph nodes > 2 cm a LRC benefit of 15% at 2 years should be expected. The ESCALOX trial is supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG); Grant No.: MO-363/4-1.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov Identifier: NCT 01212354 , EudraCT-No.: 2010-021139-15.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT01212354.
Keywords: Chemo-irradiation; Dose escalation; Head and neck cancer; Randomized prospective trial.
Similar articles
-
[SIB-IMRT radiotherapy given concomitantly with cisplatin for locally advanced squamous cell head and neck cancer (SCHNC). Evaluation of the early results and toxicity].Otolaryngol Pol. 2011 Sep;65(5 Suppl):117-25. doi: 10.1016/S0030-6657(11)70719-3. Otolaryngol Pol. 2011. PMID: 22000261 Polish.
-
Simultaneous integrated boost intensity-modulated radiotherapy for locally advanced head-and-neck squamous cell carcinomas: II--clinical results.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004 Oct 1;60(2):374-87. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2004.03.010. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2004. PMID: 15380569 Clinical Trial.
-
Phase II/III Randomized Controlled Trial of Concomitant Hyperfractionated Radiotherapy plus Cetuximab (Anti-EGFR Antibody) or Chemotherapy in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer.Gulf J Oncolog. 2019 May;1(30):6-12. Gulf J Oncolog. 2019. PMID: 31242976 Clinical Trial.
-
Second infield re-irradiation with a resulting cumulative equivalent dose (EQD2max ) of >180 Gy for patients with recurrent head and neck cancer.Head Neck. 2019 Apr;41(4):E48-E54. doi: 10.1002/hed.25428. Epub 2018 Dec 6. Head Neck. 2019. PMID: 30521102 Review.
-
A Review of Modern Radiation Therapy Dose Escalation in Locally Advanced Head and Neck Cancer.Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2020 May;32(5):330-341. doi: 10.1016/j.clon.2019.12.004. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol). 2020. PMID: 31911016 Review.
Cited by
-
Early Response Prediction of Multiparametric Functional MRI and 18F-FDG-PET in Patients with Head and Neck Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with (Chemo)Radiation.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Jan 3;14(1):216. doi: 10.3390/cancers14010216. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35008380 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting hypoxia status using a combination of contrast-enhanced computed tomography and [18F]-Fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography radiomics features.Radiother Oncol. 2018 Apr;127(1):36-42. doi: 10.1016/j.radonc.2017.11.025. Epub 2017 Dec 19. Radiother Oncol. 2018. PMID: 29273260 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the impact of metabolic imaging in head and neck cancer treatment.Head Neck. 2022 Oct;44(10):2228-2247. doi: 10.1002/hed.27131. Epub 2022 Jul 1. Head Neck. 2022. PMID: 35775713 Free PMC article.
-
FMISO-Based Adaptive Radiotherapy in Head and Neck Cancer.J Pers Med. 2022 Jul 29;12(8):1245. doi: 10.3390/jpm12081245. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36013194 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Use of Quantitative Imaging in Radiation Oncology: A Quantitative Imaging Network (QIN) Perspective.Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018 Nov 15;102(4):1219-1235. doi: 10.1016/j.ijrobp.2018.06.023. Epub 2018 Jun 30. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2018. PMID: 29966725 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- (Hrsg.) ZfKiRK-I . Bericht zum Krebsgeschehen in Deutschland 2016. In: Koch-Institut ZfKiR, editor. Bericht zum Krebsgeschehen in Deutschland 2016. Berlin: Robert-Koch-Institut; 2016.
-
- Pignon JP, Bourhis J, Domenge C, Designe L. Chemotherapy added to locoregional treatment for head and neck squamous-cell carcinoma: three meta-analyses of updated individual data. MACH-NC Collaborative Group. Meta-Analysis of Chemotherapy on Head and Neck Cancer. Lancet. 2000;355(9208):949–955. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(00)90011-4. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical