Effect of Dexmedetomidine combined with sufentanil for post- thoracotomy intravenous analgesia:a randomized, controlled clinical study
- PMID: 28249614
- PMCID: PMC5333470
- DOI: 10.1186/s12871-017-0324-4
Effect of Dexmedetomidine combined with sufentanil for post- thoracotomy intravenous analgesia:a randomized, controlled clinical study
Abstract
Background: Few studies have investigated the use of dexmedetomidine in patient-controlled intravenous analgesia (PCIA) after thoracic surgery. This study to evaluate the effect of dexmedetomidine combined with sufentanil for PCIA after thoracotomy under general anaesthesia.
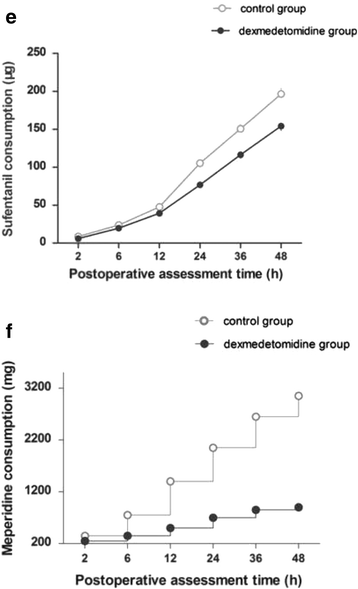
Methods: Ninety-seven adults patients scheduled for thoracotomy surgery. All two groups received PCIA with either sufentanil alone (control group) or combining dexmedetomidine with sufentanil (dexmedetomidine group). Hemodynamic measurements, visual analog scale (VAS) scores at rest and at coughing, Ramsay sedation score (RSS), analgesic consumption, and postoperative nausea and vomiting (PONV) as well as drug-related adverse effects were compared at 2, 6, 12, 24, 36 and 48 h postoperatively.
Results: In the patients of the dexmedetomidine group, compared to the control group, the pain scores at rest or at coughing during 48 h postoperatively were lower (P < 0.001), the sedation scores were lower, the consumption of sufentanil and rescue meperidine were lower, and the number of episode of moderate PONV was three times lower. No signs of toxicity or local complications were observed. There was a non-significant trend for a lower HR and BP in the dexmedetomidine group vs.
Conclusion: The combining dexmedetomidine with sufentanil for post-thoracotomy PCIA can improve pain control together with the decrease in sufentanil requirements, and improve postoperative patient's satisfaction compared with sufentanil alone in PCIA.
Trial registration: This trial was retrospectively registered on 27 April 2016 at the Chinese Clinical Trial Register (number: ChiCTR-ONC-16008376 ).
Keywords: Combination; Dexmedetomidine; Intravenous analgesia; Post-thoracotomy; Sufentanil.
Figures





Similar articles
-
Dexmedetomidine combined with sufentanil and dezocine-based patient-controlled intravenous analgesia increases female patients' global satisfaction degree after thoracoscopic surgery.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 Apr 21;16(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01472-4. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 33882970 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Patient-controlled Intravenous Analgesia With Combination of Dexmedetomidine and Sufentanil on Patients After Abdominal Operation: A Prospective, Randomized, Controlled, Blinded, Multicenter Clinical Study.Clin J Pain. 2018 Feb;34(2):155-161. doi: 10.1097/AJP.0000000000000527. Clin J Pain. 2018. PMID: 28654556 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of dexmedetomidine combined with sufentanil for post-caesarean section intravenous analgesia: a randomised, placebo-controlled study.Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014 Apr;31(4):197-203. doi: 10.1097/EJA.0000000000000011. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2014. PMID: 24463478 Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy and safety of dexmedetomidine combined with tramadol for patient-controlled intravenous analgesia in Chinese surgical patients: A systematic review and meta-analysis.Medicine (Baltimore). 2020 Jan;99(3):e18825. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000018825. Medicine (Baltimore). 2020. PMID: 32011494 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine and sufentanil combination versus sufentanil alone for postoperative intravenous patient-controlled analgesia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials.BMC Anesthesiol. 2019 May 18;19(1):81. doi: 10.1186/s12871-019-0756-0. BMC Anesthesiol. 2019. PMID: 31103031 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Efficacy of dexmedetomidine in reducing post-operative pain and improving the quality of recovery in patients with burn wounds undergoing tangential excision skin grafting.Exp Ther Med. 2019 Mar;17(3):1776-1782. doi: 10.3892/etm.2019.7155. Epub 2019 Jan 7. Exp Ther Med. 2019. PMID: 30783449 Free PMC article.
-
Dexmedetomidine combined with sufentanil and dezocine-based patient-controlled intravenous analgesia increases female patients' global satisfaction degree after thoracoscopic surgery.J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021 Apr 21;16(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s13019-021-01472-4. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2021. PMID: 33882970 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Perioperative Dexmedetomidine Fails to Improve Postoperative Analgesic Consumption and Postoperative Recovery in Patients Undergoing Lateral Thoracotomy for Thoracic Esophageal Cancer: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial.Pain Res Manag. 2020 May 6;2020:4145893. doi: 10.1155/2020/4145893. eCollection 2020. Pain Res Manag. 2020. PMID: 32454920 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Comparison of the Preemptive/Preventive Effect of Dexmedetomidine and Ketorolac on Post-operative Pain of Appendectomy Patients: A Randomized Clinical Trial.Anesth Pain Med. 2024 Dec 16;14(6):e146868. doi: 10.5812/aapm-146868. eCollection 2024 Dec. Anesth Pain Med. 2024. PMID: 40078643 Free PMC article.
-
Ropivacaine versus ropivacaine plus dexmedetomidine in serratus anterior plane block patients undergoing post-thoracotomy surgery: a randomized, double-blinded clinical trial.BMC Anesthesiol. 2024 Oct 30;24(1):391. doi: 10.1186/s12871-024-02769-2. BMC Anesthesiol. 2024. PMID: 39478458 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Unlugenc H, Tetiker S, Buyukkurt S, Guler T, Isik G. Comparison of the effect of adding remifentanil to patient-controlled tramadol or morphine for postoperative analgesia after major abdominal surgery. J Opioid Manag. 2009;5(5):247–255. - PubMed
-
- Blaudszun G, Lysakowski C, Elia N, Tramer MR. Effect of perioperative systemic α2 agonists on postoperative morphine consumption and pain intensity: systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Anesthesiology. 2012;116(6):1312–1322. doi: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e31825681cb. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

