High levels of serum β2-microglobulin predict severity of coronary artery disease
- PMID: 28249620
- PMCID: PMC5333396
- DOI: 10.1186/s12872-017-0502-9
High levels of serum β2-microglobulin predict severity of coronary artery disease
Abstract
Background: The identification of new risk factors for coronary artery disease (CAD) is increasingly sought in an effort to tackle this threatening disease. β2-microglobulin (B2M) is reported to associate with peripheral arterial disease and adverse cardiovascular outcomes. However, the association between B2M and cardiovascular disease remains under-researched. This study evaluated the effects of B2M on CAD without renal dysfunction.
Methods: One thousand seven hundred sixty-two subjects (403 non-CAD subjects and 1,359 CAD subjects) were investigated. Fasting samples were collected to determine B2M level. The Gensini and SYNTAX scores were used to assess the severity of CAD.
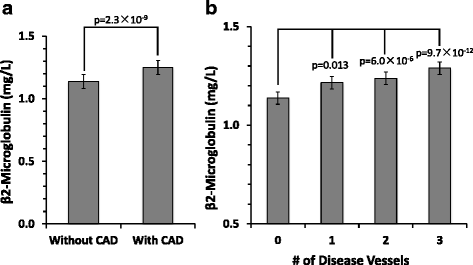
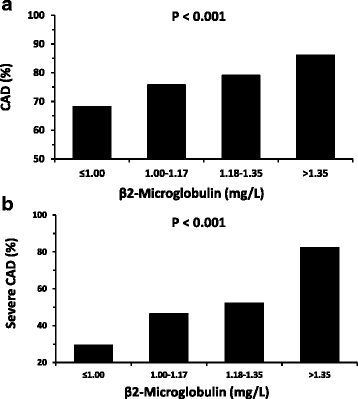
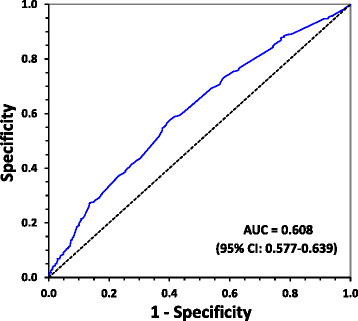
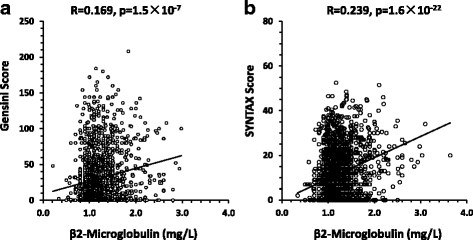
Results: CAD subjects were significantly higher in serum B2M level comparing with non-CAD subjects (1.25 ± 0.46 vs 1.14 ± 0.28 mg/L, p < 0.001). Serum B2M level was a risk factor of CAD after adjusting potential confounders (Odds Ratio (OR) = 2.363, 95% confidence interval (CI): 1.467-3.906, p = 0.001). Receiver operating characteristics (ROC) showed B2M level moderately predicted diagnosis of CAD (the area under the ROC curve (AUC) = 0.608, 95% CI: 0.577-0.639, p < 0.001). Furthermore, serum B2M level was positively associated with Gensini score system, SYNTAX score system and the number of disease vessels (NDV ≥ 2).
Conclusions: The significant association between serum B2M and CAD suggests that B2M could be a biomarker for CAD.
Keywords: Coronary artery disease; Severity; β2-Microglobulin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Increased serum concentrations of pentosidine are related to presence and severity of coronary artery disease.Thromb Res. 2014 Sep;134(3):633-8. doi: 10.1016/j.thromres.2014.07.008. Epub 2014 Jul 17. Thromb Res. 2014. PMID: 25065554
-
SYNTAX score-0 patients: risk stratification in nonobstructive coronary artery disease.Clin Res Cardiol. 2016 Nov;105(11):901-911. doi: 10.1007/s00392-016-0998-5. Epub 2016 Jun 30. Clin Res Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27364941
-
Increased Serum Level of Growth Differentiation Factor 15 (GDF-15) is Associated with Coronary Artery Disease.Cardiovasc Ther. 2016 Jun;34(3):138-43. doi: 10.1111/1755-5922.12184. Cardiovasc Ther. 2016. PMID: 26996787
-
Beta 2-Microglobulin and the Severity of Coronary Stenosis in Patients With Acute Coronary Syndrome.Heart Lung Circ. 2019 Apr;28(4):575-582. doi: 10.1016/j.hlc.2018.02.016. Epub 2018 Mar 5. Heart Lung Circ. 2019. PMID: 29573958
-
The Role of Beta2-Microglobulin in Central Nervous System Disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 May 14;44(1):46. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01481-6. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38743119 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Association of Beta-2 Microglobulin with Stroke and All-Cause Mortality in Adults Aged ≥40 in U.S.: NHANES III.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Feb 2;24(2):43. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2402043. eCollection 2023 Feb. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39077409 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of Blood-Derived Factors in Protection and Regeneration of Aged Tissues.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Aug 25;23(17):9626. doi: 10.3390/ijms23179626. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36077021 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between serum β2-microglobulin and left ventricular hypertrophy in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: A cross-sectional study.J Diabetes. 2024 Aug;16(8):e13599. doi: 10.1111/1753-0407.13599. J Diabetes. 2024. PMID: 39155680 Free PMC article.
-
Predictive value of serum β2-microglobulin in cardiac valve calcification in maintenance hemodialysis patients.J Thorac Dis. 2023 Sep 28;15(9):4914-4924. doi: 10.21037/jtd-23-1185. Epub 2023 Sep 22. J Thorac Dis. 2023. PMID: 37868894 Free PMC article.
-
IRF1-mediated downregulation of PGC1α contributes to cardiorenal syndrome type 4.Nat Commun. 2020 Sep 16;11(1):4664. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-18519-0. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32938919 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Beltrame JF, Weekes AJ, Morgan C, Tavella R, Spertus JA. The prevalence of weekly angina among patients with chronic stable angina in primary care practices: The Coronary Artery Disease in General Practice (CADENCE) Study. Arch Intern Med. 2009;169(16):1491–1499. doi: 10.1001/archinternmed.2009.295. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Haverkate F, Thompson SG, Pyke SD, Gallimore JR, Pepys MB. Production of C-reactive protein and risk of coronary events in stable and unstable angina. European Concerted Action on Thrombosis and Disabilities Angina Pectoris Study Group. Lancet. 1997;349(9050):462–466. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(96)07591-5. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Dibra A, Mehilli J, Braun S, Hadamitzky M, Baum H, Dirschinger J, Schuhlen H, Schomig A, Kastrati A. Association between C-reactive protein levels and subsequent cardiac events among patients with stable angina treated with coronary artery stenting. Am J Med. 2003;114(9):715–722. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9343(03)00183-9. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

