Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer
- PMID: 28249908
- PMCID: PMC5421398
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-2653
Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer
Erratum in
-
Correction: Kinome-Wide RNA Interference Screen Reveals a Role for PDK1 in Acquired Resistance to CDK4/6 Inhibition in ER-Positive Breast Cancer.Cancer Res. 2019 Feb 15;79(4):874. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-18-4086. Cancer Res. 2019. PMID: 30770369 No abstract available.
Abstract
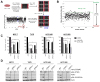
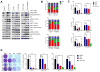
Acquired resistance to cyclin-dependent kinases 4 and 6 (CDK4/6) small-molecule inhibitors in breast cancer arises through mechanisms that are yet uncharacterized. In this study, we used a kinome-wide siRNA screen to identify kinases that, when downregulated, yield sensitivity to the CDK4/6 inhibitor ribociclib. In this manner, we identified 3-phosphoinositide-dependent protein kinase 1 (PDK1) as a key modifier of ribociclib sensitivity in estrogen receptor-positive MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Pharmacologic inhibition of PDK1 with GSK2334470 in combination with ribociclib or palbociclib, another CDK4/6 inhibitor, synergistically inhibited proliferation and increased apoptosis in a panel of ER-positive breast cancer cell lines. Ribociclib-resistant breast cancer cells selected by chronic drug exposure displayed a relative increase in the levels of PDK1 and activation of the AKT pathway. Analysis of these cells revealed that CDK4/6 inhibition failed to induce cell-cycle arrest or senescence. Mechanistic investigations showed that resistant cells coordinately upregulated expression of cyclins A, E, and D1, activated phospho-CDK2, and phospho-S477/T479 AKT. Treatment with GSK2334470 or the CDK2 inhibitor dinaciclib was sufficient to reverse these events and to restore the sensitivity of ribociclib-resistant cells to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Ribociclib, in combination with GSK2334470 or the PI3Kα inhibitor alpelisib, decreased xenograft tumor growth more potently than each drug alone. Taken together, our results highlight a role for the PI3K-PDK1 signaling pathway in mediating acquired resistance to CDK4/6 inhibitors. Cancer Res; 77(9); 2488-99. ©2017 AACR.
©2017 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Finn RS, Crown JP, Lang I, Boer K, Bondarenko IM, Kulyk SO, et al. The cyclin-dependent kinase 4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in combination with letrozole versus letrozole alone as first-line treatment of oestrogen receptor-positive, HER2-negative, advanced breast cancer (PALOMA-1/TRIO-18): a randomised phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol. 2015;16:25–35. - PubMed
-
- Infante JR, Shapiro G, Witteveen P, Gerecitano JF, Ribrag V, Chugh R, et al. A phase I study of the single-agent CDK4/6 inhibitor LEE011 in pts with advanced solid tumors and lymphomas. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2014:32.
-
- Shapiro G, Rosen LS, Tolcher AW, Goldman JW, Gandhi L, Papadopoulos KP, et al. A first-in-human phase I study of the CDK4/6 inhibitor, LY2835219, for patients with advanced cancer. Journal of Clinical Oncology. 2013:31.
-
- Turner NC, Huang Bartlett C, Cristofanilli M. Palbociclib in Hormone-Receptor-Positive Advanced Breast Cancer. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:1672–3. - PubMed
-
- Patnaik A, Rosen LS, Tolaney SM, Tolcher AW, Goldman JW, Gandhi L, et al. Efficacy and Safety of Abemaciclib, an Inhibitor of CDK4 and CDK6, for Patients with Breast Cancer, Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer, and Other Solid Tumors. Cancer discovery. 2016;6:740–53. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

