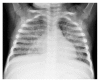
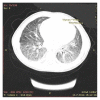
Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis in a Child with Recurrent Macrophage Activation Syndrome Secondary to Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
- PMID: 28251009
- PMCID: PMC5303873
- DOI: 10.1155/2017/5693501
Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis in a Child with Recurrent Macrophage Activation Syndrome Secondary to Systemic Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis
Abstract
Macrophage activation syndrome, a severe complication of systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis and other inflammatory diseases, represents one of the most important rheumatological emergencies. Delayed diagnosis could lead to life-threatening complications. Pulmonary hemosiderosis has been classically characterized by a triad of anemia, hemoptysis, and lung infiltrates on chest radiogram. Although the majority of patients of pulmonary hemosiderosis are considered idiopathic, secondary hemosiderosis associated with known diseases could be seen. In this case report, we aimed to present gradually increased pulmonary manifestations due to pulmonary hemosiderosis with recurrent macrophage activation syndrome attacks in a child with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Place of bronchoscopy in the diagnostics and follow-up of patients with idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis.Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2021 Aug 31;63(4):582-585. doi: 10.3897/folmed.63.e56088. Folia Med (Plovdiv). 2021. PMID: 35851160
-
Juvenile idiopathic arthritis with pulmonary hemosiderosis: a case report.J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002 Jun;35(2):133-5. J Microbiol Immunol Infect. 2002. PMID: 12099336
-
Disease recurrence after lung transplantation for idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis.Respir Med Case Rep. 2020 Jun 10;30:101128. doi: 10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101128. eCollection 2020. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020. PMID: 32577369 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and alveolar hemorrhage syndrome: case report and review of the literature.S D J Med. 1995 Mar;48(3):79-85. S D J Med. 1995. PMID: 7740300 Review.
-
Recognition and management of macrophage activation syndrome in juvenile arthritis.Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007 Sep;19(5):477-81. doi: 10.1097/BOR.0b013e32825a6a79. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2007. PMID: 17762614 Review.
Cited by
-
Interleukin (IL)-1/IL-6-Inhibitor-Associated Drug Reaction With Eosinophilia and Systemic Symptoms (DReSS) in Systemic Inflammatory Illnesses.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024 Nov;12(11):2996-3013.e7. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.07.002. Epub 2024 Aug 15. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024. PMID: 39002722
-
Cytokine Storm Syndrome Responsive to IL-1 Inhibition in Trisomy 21.Case Rep Pediatr. 2024 Mar 28;2024:9946401. doi: 10.1155/2024/9946401. eCollection 2024. Case Rep Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 38577256 Free PMC article.
-
Successful Liposteroid Therapy for a Recurrent Idiopathic Pulmonary Hemosiderosis with Down Syndrome.Case Rep Pediatr. 2020 Apr 25;2020:5292947. doi: 10.1155/2020/5292947. eCollection 2020. Case Rep Pediatr. 2020. PMID: 32373381 Free PMC article.
-
Idiopathic pulmonary hemosiderosis and stroke secondary to protein C deficiency in a child with Down syndrome: a case report.J Med Case Rep. 2023 Mar 11;17(1):105. doi: 10.1186/s13256-023-03807-2. J Med Case Rep. 2023. PMID: 36899396 Free PMC article.
-
Macrophage activation syndrome in a Sudanese child: a case report from Sudan.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024 Mar 6;86(5):3047-3051. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000001900. eCollection 2024 May. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2024. PMID: 38694344 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Barut K., Yücel G., Sinoplu A. B., Şahin S., Adroviç A., Kasapçopur Ö. Evaluation of macrophage activation syndrome associated with systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: single center experience over a one-year period. Turkish Archives of Pediatrics. 2015;50(4):206–210. doi: 10.5152/turkpediatriars.2015.3299. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Minoia F., Davì S., Horne A., et al. Clinical features, treatment, and outcome of macrophage activation syndrome complicating systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis: a multinational, multicenter study of 362 patients. Arthritis and Rheumatology. 2014;66(11):3160–3169. doi: 10.1002/art.38802. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources