Petroselinum Crispum is Effective in Reducing Stress-Induced Gastric Oxidative Damage
- PMID: 28251024
- PMCID: PMC5322505
- DOI: 10.4274/balkanmedj.2015.1411
Petroselinum Crispum is Effective in Reducing Stress-Induced Gastric Oxidative Damage
Abstract
Background: Oxidative stress has been shown to play a principal role in the pathogenesis of stress-induced gastric injury. Parsley (Petroselinum crispum) contains many antioxidants such as flavanoids, carotenoids and ascorbic acid.
Aims: In this study, the histopathological and biochemical results of nutrition with a parsley-rich diet in terms of eliminating stress-induced oxidative gastric injury were evaluated.
Study design: Animal experimentation.
Methods: Forty male Wistar albino rats were divided into five groups: control, stress, stress + standard diet, stress + parsley-added diet and stress + lansoprazole (LPZ) groups. Subjects were exposed to 72 hours of fasting and later immobilized and exposed to the cold at +4 degrees for 8 hours to create a severe stress condition. Samples from the animals' stomachs were arranged for microscopic and biochemical examinations.
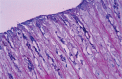
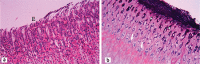
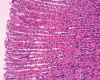
Results: Gastric mucosal injury was obvious in rats exposed to stress. The histopathologic damage score of the stress group (7.00±0.57) was higher than that of the control group (1.50±0.22) (p<0.05). Significant differences in histopathologic damage score were found between the stress and stress + parsley-added diet groups (p<0.05), the stress and stress + standard diet groups (p<0.05), and the stress and stress + LPZ groups (p<0.05). The mean tissue malondialdehyde levels of the stress + parsley-added group and the stress + LPZ group were lower than that of the stress group (p<0.05). Parsley supported the cellular antioxidant system by increasing the mean tissue glutathione level (53.31±9.50) and superoxide dismutase (15.18±1.05) and catalase (16.68±2.29) activities.
Conclusion: Oral administration of parsley is effective in reducing stress-induced gastric injury by supporting the cellular antioxidant defence system.
Keywords: Lansoprazole; gastric oxidative damages; parsley.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: No conflict of interest was declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Bandyopadhyay D, Chattopadhyay A. Reactive oxygen species-induced gastric ulceration: protection by melatonin. Curr Med Chem. 2006;13:1187–202. - PubMed
-
- Jia YT, Ma B, Wei W, Xu Y, Wang Y, Tang HT, et al. Sustained activation of nuclear factor-kappaB by reactive oxygen species is involved in the pathogenesis of stress-induced gastric damage in rats. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:1582–91. - PubMed
-
- Jia YT, Wei W, Ma B, Xu Y, Liu WJ, Wang Y, et al. Activation of p38 MAPK by reactive oxygen species is essential in a rat model of stress-induced gastric mucosal injury. J Immunol. 2007;179:7808–19. - PubMed
-
- Sahin E, Gümüşlü S. Stress-dependent induction of protein oxidation, lipid peroxidation and anti-oxidants in peripheral tissues of rats: comparison of three stress models (immobilization, cold and immobilization-cold) Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2007;34:425–31. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
