Improved recognition of ineffective chest compressions after a brief Crew Resource Management (CRM) training: a prospective, randomised simulation study
- PMID: 28253848
- PMCID: PMC5335734
- DOI: 10.1186/s12873-017-0117-6
Improved recognition of ineffective chest compressions after a brief Crew Resource Management (CRM) training: a prospective, randomised simulation study
Abstract
Background: Chest compressions are a core element of cardio-pulmonary resuscitation. Despite periodic training, real-life chest compressions have been reported to be overly shallow and/or fast, very likely affecting patient outcomes. We investigated the effect of a brief Crew Resource Management (CRM) training program on the correction rate of improperly executed chest compressions in a simulated cardiac arrest scenario.
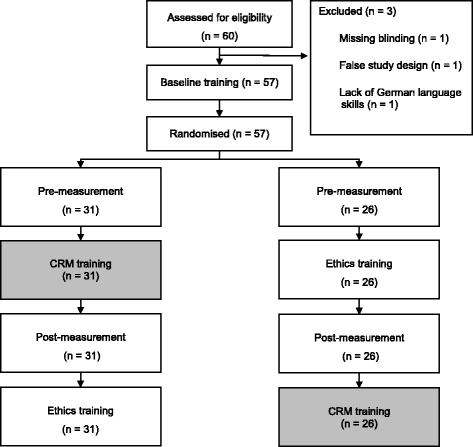
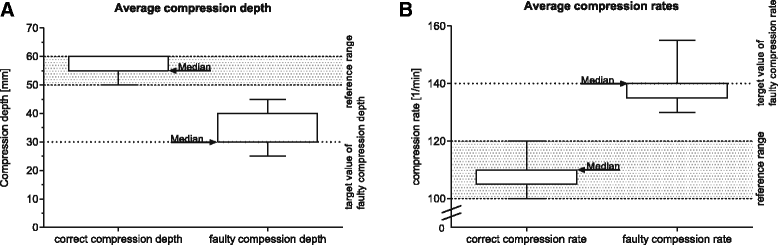
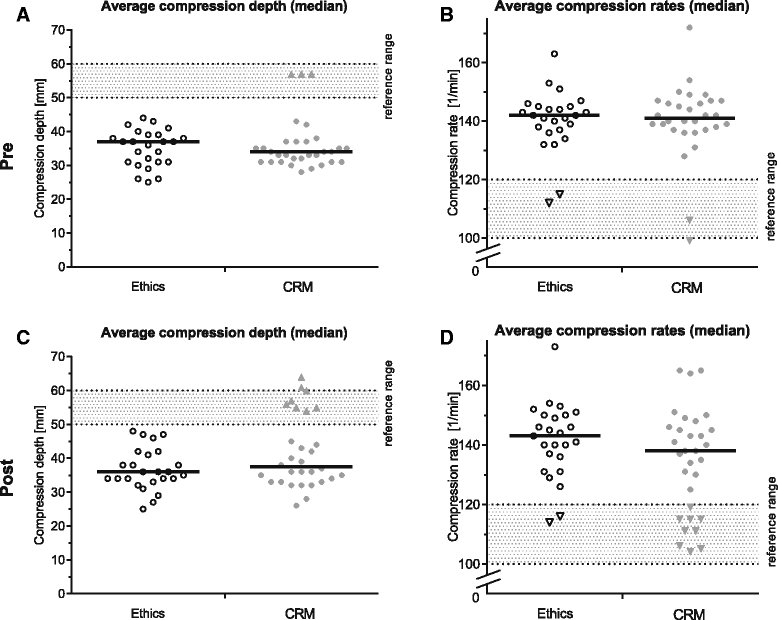
Methods: Final-year medical students (n = 57) were randomised to receive a 10-min computer-based CRM or a control training on ethics. Acting as team leaders, subjects performed resuscitation in a simulated cardiac arrest scenario before and after the training. Team members performed standardised overly shallow and fast chest compressions. We analysed how often the team leader recognised and corrected improper chest compressions, as well as communication and resuscitation quality.
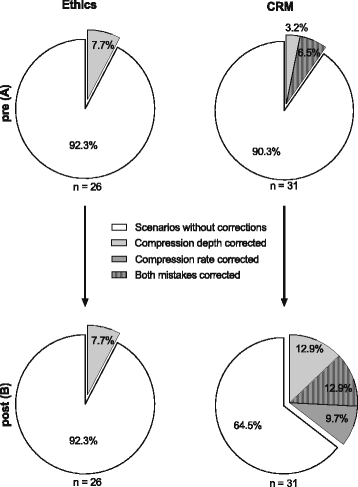
Results: After the CRM training, team leaders corrected improper chest compressions (35.5%) significantly more often compared with those undergoing control training (7.7%, p = 0.03*). Consequently, four students have to be trained (number needed to treat = 3.6) for one improved chest compression scenario. Communication quality assessed by the Leader Behavior Description Questionnaire significantly increased in the intervention group by a mean of 4.5 compared with 2.0 (p = 0.01*) in the control group.
Conclusion: A computer-based, 10-min CRM training improved the recognition of ineffective of chest compressions. Furthermore, communication quality increased. As guideline-adherent chest compressions have been linked to improved patient outcomes, our CRM training might represent a brief and affordable approach to increase chest compression quality and potentially improve patient outcomes.
Keywords: Cardiopulmonary resuscitation; Communication; Crew resource management; Emergency medicine; Healthcare; Hospital rapid response team; Simulation training.
Figures

References
-
- Perkins GD, Handley AJ, Koster RW, Castrén M, Smyth MA, Olasveengen T, Monsieurs KG, Raffay V, Gräsner J-T, Wenzel V. European Resuscitation Council Guidelines for Resuscitation 2015: Section 2. Adult basic life support and automated external defibrillation. Resuscitation. 2015;95:81–99. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2015.07.015. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Edelson DP, Abella BS, Kramer-Johansen J, Wik L, Myklebust H, Barry AM, Merchant RM, Hoek TLV, Steen PA, Becker LB. Effects of compression depth and pre-shock pauses predict defibrillation failure during cardiac arrest. Resuscitation. 2006;71(2):137–145. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2006.04.008. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

