IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang
- PMID: 28254169
- PMCID: PMC5411326
- DOI: 10.1016/j.it.2017.01.006
IL-17 Signaling: The Yin and the Yang
Abstract
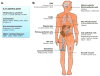
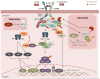
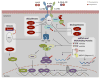
Interleukin (IL)-17 is the founding member of a novel family of inflammatory cytokines. While the proinflammatory properties of IL-17 are key to its host-protective capacity, unrestrained IL-17 signaling is associated with immunopathology, autoimmune disease, and cancer progression. In this review we discuss both the activators and the inhibitors of IL-17 signal transduction, and also the physiological implications of these events. We highlight the surprisingly diverse means by which these regulators control expression of IL-17-dependent inflammatory genes, as well as the major target cells that respond to IL-17 signaling.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
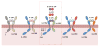
References
-
- Rouvier E, et al. CTLA-8, cloned from an activated T cell, bearing AU-rich messenger RNA instability sequences, and homologous to a Herpesvirus Saimiri gene. J Immunol. 1993;150:5445–5456. - PubMed
-
- Cua DJ, et al. Interleukin-23 rather than interleukin-12 is the critical cytokine for autoimmune inflammation of the brain. Nature. 2003;421(6924):744–8. - PubMed
-
- Harrington LE, et al. Interleukin 17-producing CD4+ effector T cells develop via a lineage distinct from the T helper type 1 and 2 lineages. Nat Immunol. 2005;6(11):1123–32. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

