Gene expression profiling in the human alcoholic brain
- PMID: 28254370
- PMCID: PMC5479716
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuropharm.2017.02.017
Gene expression profiling in the human alcoholic brain
Abstract
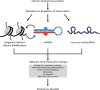
Long-term alcohol use causes widespread changes in gene expression in the human brain. Aberrant gene expression changes likely contribute to the progression from occasional alcohol use to alcohol use disorder (including alcohol dependence). Transcriptome studies have identified individual gene candidates that are linked to alcohol-dependence phenotypes. The use of bioinformatics techniques to examine expression datasets has provided novel systems-level approaches to transcriptome profiling in human postmortem brain. These analytical advances, along with recent developments in next-generation sequencing technology, have been instrumental in detecting both known and novel coding and non-coding RNAs, alternative splicing events, and cell-type specific changes that may contribute to alcohol-related pathologies. This review offers an integrated perspective on alcohol-responsive transcriptional changes in the human brain underlying the regulatory gene networks that contribute to alcohol dependence. This article is part of the Special Issue entitled "Alcoholism".
Keywords: Alcohol; Co-expression networks; Gene expression; RNA-seq; Transcriptional regulation.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Adachi Y, Moore LE, Bradford BU, Gao W, Thurman RG. Antibiotics prevent liver injury in rats following long-term exposure to ethanol. Gastroenterology. 1995;108:218–224. - PubMed
-
- Alaux-Cantin S, Warnault V, Legastelois R, Botia B, Pierrefiche O, Vilpoux C, Naassila M. Alcohol intoxications during adolescence increase motivation for alcohol in adult rats and induce neuroadaptations in the nucleus accumbens. Neuropharmacology. 2013;67:521–531. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

