Pediatric Blepharoptosis
- PMID: 28255291
- PMCID: PMC5330798
- DOI: 10.1055/s-0037-1598631
Pediatric Blepharoptosis
Abstract
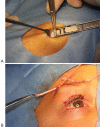
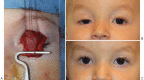
Congenital blepharoptosis, caused by levator muscle dysgenesis, presents at birth and may lead to disturbed visual development and function. Other causes of ptosis in pediatric patients can be myogenic, neurogenic, mechanical, or traumatic. Timely correction is, therefore, critical, and careful preoperative planning and intraoperative considerations are crucial to achieve optimal outcomes and minimize potential complications. The various surgical techniques, including the frontalis suspension or sling, levator resection and advancement, Müller's muscle conjunctival resection (the Putterman procedure), and modified Fasanella-Servat procedure are each associated with distinct indications, benefits, and drawbacks, necessitating a unique tailored approach to each surgical candidate.
Keywords: blepharoptosis; droopy eyelid; pediatric ptosis.
Figures



References
-
- El Essawy R, Elsada M A. Clinical and demographic characteristics of ptosis in children: a national tertiary hospital study. Eur J Ophthalmol. 2013;23(3):356–360. - PubMed
-
- Berry-Brincat A, Willshaw H. Paediatric blepharoptosis: a 10-year review. Eye (Lond) 2009;23(7):1554–1559. - PubMed
-
- Lemagne J M, Colonval S, Moens B, Brucher J M. [Anatomical modification of the levator muscle of the eyelid in congenital ptosis] Bull Soc Belge Ophtalmol. 1992;243:23–27. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

