MicroRNA Detection Using a Double Molecular Beacon Approach: Distinguishing Between miRNA and Pre-miRNA
- PMID: 28255356
- PMCID: PMC5327639
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.16840
MicroRNA Detection Using a Double Molecular Beacon Approach: Distinguishing Between miRNA and Pre-miRNA
Abstract
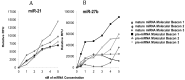
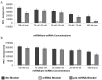
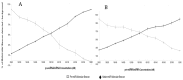
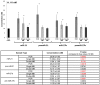
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, noncoding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression and are recognized for their roles both as modulators of disease progression and as biomarkers of disease activity, including neurological diseases, cancer, and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Commonly, miRNA abundance is assessed using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), however, qRT-PCR for miRNA can be labor intensive, time consuming, and may lack specificity for detection of mature versus precursor forms of miRNA. Here, we describe a novel double molecular beacon approach to miRNA assessment that can distinguish and quantify mature versus precursor forms of miRNA in a single assay, an essential feature for use of miRNAs as biomarkers for disease. Using this approach, we found that molecular beacons with DNA or combined locked nucleic acid (LNA)-DNA backbones can detect mature and precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) of low (< 1 nM) abundance in vitro. The double molecular beacon assay was accurate in assessing miRNA abundance in a sample containing a mixed population of mature and precursor miRNAs. In contrast, qRT-PCR and the single molecular beacon assay overestimated miRNA abundance. Additionally, the double molecular beacon assay was less labor intensive than traditional qRT-PCR and had 10-25% increased specificity. Our data suggest that the double molecular beacon-based approach is more precise and specific than previous methods, and has the promise of being the standard for assessing miRNA levels in biological samples.
Keywords: PCR.; cardiovascular disease; molecular beacon, microRNA, microRNA detection.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




Similar articles
-
In vitro quantification of specific microRNA using molecular beacons.Nucleic Acids Res. 2012 Jan;40(2):e13. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr1016. Epub 2011 Nov 21. Nucleic Acids Res. 2012. PMID: 22110035 Free PMC article.
-
The use of molecular beacons to detect and quantify microRNA.Methods Mol Biol. 2013;1039:279-87. doi: 10.1007/978-1-62703-535-4_22. Methods Mol Biol. 2013. PMID: 24026703
-
In situ single step detection of exosome microRNA using molecular beacon.Biomaterials. 2015 Jun;54:116-25. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.03.014. Epub 2015 Mar 31. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25907045
-
Isothermal Amplification for MicroRNA Detection: From the Test Tube to the Cell.Acc Chem Res. 2017 Apr 18;50(4):1059-1068. doi: 10.1021/acs.accounts.7b00040. Epub 2017 Mar 29. Acc Chem Res. 2017. PMID: 28355077 Review.
-
Real-time PCR quantification of precursor and mature microRNA.Methods. 2008 Jan;44(1):31-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ymeth.2007.09.006. Methods. 2008. PMID: 18158130 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Sensitively distinguishing intracellular precursor and mature microRNA abundance.Chem Sci. 2018 Nov 28;10(6):1709-1715. doi: 10.1039/c8sc03305f. eCollection 2019 Feb 14. Chem Sci. 2018. PMID: 30842835 Free PMC article.
-
Size-selective molecular recognition based on a confined DNA molecular sieve using cavity-tunable framework nucleic acids.Nat Commun. 2020 Mar 23;11(1):1518. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-15297-7. Nat Commun. 2020. PMID: 32251279 Free PMC article.
-
Decrease in Lymphoid Specific Helicase and 5-hydroxymethylcytosine Is Associated with Metastasis and Genome Instability.Theranostics. 2017 Sep 5;7(16):3920-3932. doi: 10.7150/thno.21389. eCollection 2017. Theranostics. 2017. PMID: 29109788 Free PMC article.
-
Catalytic hairpin assembly gel assay for multiple and sensitive microRNA detection.Theranostics. 2018 Apr 3;8(10):2646-2656. doi: 10.7150/thno.24480. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29774065 Free PMC article.
-
Rapid and ultrasensitive miRNA detection by combining endonuclease reactions in a rolling circle amplification (RCA)-based hairpin DNA fluorescent assay.Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023 Apr;415(10):1991-1999. doi: 10.1007/s00216-023-04618-6. Epub 2023 Feb 28. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2023. PMID: 36853410
References
-
- Dennis C. The brave new world of RNA. Nature. 2002;418:122–4. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- van Rooij E. The art of microRNA research. Circulation research. 2011;108:219–34. - PubMed
-
- Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2006;13:1097–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

