MicroRNA Detection Using a Double Molecular Beacon Approach: Distinguishing Between miRNA and Pre-miRNA
- PMID: 28255356
- PMCID: PMC5327639
- DOI: 10.7150/thno.16840
MicroRNA Detection Using a Double Molecular Beacon Approach: Distinguishing Between miRNA and Pre-miRNA
Abstract
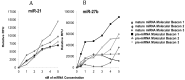
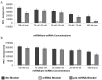
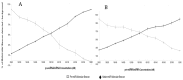
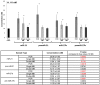
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small, noncoding RNAs that post-transcriptionally regulate gene expression and are recognized for their roles both as modulators of disease progression and as biomarkers of disease activity, including neurological diseases, cancer, and cardiovascular disease (CVD). Commonly, miRNA abundance is assessed using quantitative real-time PCR (qRT-PCR), however, qRT-PCR for miRNA can be labor intensive, time consuming, and may lack specificity for detection of mature versus precursor forms of miRNA. Here, we describe a novel double molecular beacon approach to miRNA assessment that can distinguish and quantify mature versus precursor forms of miRNA in a single assay, an essential feature for use of miRNAs as biomarkers for disease. Using this approach, we found that molecular beacons with DNA or combined locked nucleic acid (LNA)-DNA backbones can detect mature and precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) of low (< 1 nM) abundance in vitro. The double molecular beacon assay was accurate in assessing miRNA abundance in a sample containing a mixed population of mature and precursor miRNAs. In contrast, qRT-PCR and the single molecular beacon assay overestimated miRNA abundance. Additionally, the double molecular beacon assay was less labor intensive than traditional qRT-PCR and had 10-25% increased specificity. Our data suggest that the double molecular beacon-based approach is more precise and specific than previous methods, and has the promise of being the standard for assessing miRNA levels in biological samples.
Keywords: PCR.; cardiovascular disease; molecular beacon, microRNA, microRNA detection.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures




References
-
- Dennis C. The brave new world of RNA. Nature. 2002;418:122–4. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–97. - PubMed
-
- van Rooij E. The art of microRNA research. Circulation research. 2011;108:219–34. - PubMed
-
- Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL. RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nature structural & molecular biology. 2006;13:1097–101. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

