Novel small molecule inhibiting CDCP1-PKCδ pathway reduces tumor metastasis and proliferation
- PMID: 28256037
- PMCID: PMC5448658
- DOI: 10.1111/cas.13218
Novel small molecule inhibiting CDCP1-PKCδ pathway reduces tumor metastasis and proliferation
Abstract
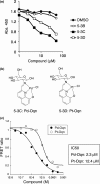
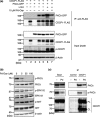
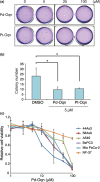
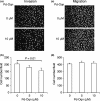
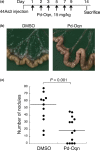
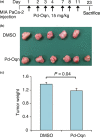
CUB domain-containing protein-1 (CDCP1) is a trans-membrane protein predominantly expressed in various cancer cells and involved in tumor progression. CDCP1 is phosphorylated at tyrosine residues in the intracellular domain by Src family kinases and recruits PKCδ to the plasma membrane through tyrosine phosphorylation-dependent association with the C2 domain of PKCδ, which in turn induces a survival signal in an anchorage-independent condition. In this study, we used our cell-free screening system to identify a small compound, glycoconjugated palladium complex (Pd-Oqn), which significantly inhibited the interaction between the C2 domain of PKCδ and phosphorylated CDCP1. Immunoprecipitation assays demonstrated that Pd-Oqn hindered the intercellular interaction of phosphorylated CDCP1 with PKCδ and also suppressed the phosphorylation of PKCδ but not that of ERK or AKT. In addition, Pd-Oqn inhibited the colony formation of gastric adenocarcinoma 44As3 cells in soft agar as well as their invasion. In mouse models, Pd-Oqn markedly reduced the peritoneal dissemination of gastric adenocarcinoma cells and the tumor growth of pancreatic cancer orthotopic xenografts. These results suggest that the novel compound Pd-Oqn reduces tumor metastasis and growth by inhibiting the association between CDCP1 and PKCδ, thus potentially representing a promising candidate among therapeutic reagents targeting protein-protein interaction.
Keywords: CDCP1; PKCδ; Src; chemical screening; metastasis.
© 2017 The Authors. Cancer Science published by John Wiley & Sons Australia, Ltd on behalf of Japanese Cancer Association.
Figures

References
-
- Scherl‐Mostageer M, Sommergruber W, Abseher R, Hauptmann R, Ambros P, Schweifer N. Identification of a novel gene, CDCP1, overexpressed in human colorectal cancer. Oncogene 2001; 20: 4402–8. - PubMed
-
- Uekita T, Sakai R. Roles of CUB domain‐containing protein 1 signaling in cancer invasion and metastasis. Cancer Sci 2011; 102: 1943–8. - PubMed
-
- Benes CH, Wu N, Elia AE, Dharia T, Cantley LC, Soltoff SP. The C2 domain of PKCdelta is a phosphotyrosine binding domain. Cell 2005; 121: 271–80. - PubMed
-
- Miyazawa Y, Uekita T, Ito Y, Seiki M, Yamaguchi H, Sakai R. CDCP1 regulates the function of MT1‐MMP and invadopodia‐mediated invasion of cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 2013; 11: 628–37. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

