SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules
- PMID: 28256516
- PMCID: PMC5335600
- DOI: 10.1038/srep42717
SwissADME: a free web tool to evaluate pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness of small molecules
Abstract
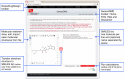
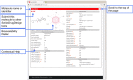
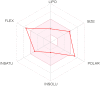
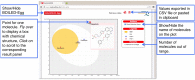
To be effective as a drug, a potent molecule must reach its target in the body in sufficient concentration, and stay there in a bioactive form long enough for the expected biologic events to occur. Drug development involves assessment of absorption, distribution, metabolism and excretion (ADME) increasingly earlier in the discovery process, at a stage when considered compounds are numerous but access to the physical samples is limited. In that context, computer models constitute valid alternatives to experiments. Here, we present the new SwissADME web tool that gives free access to a pool of fast yet robust predictive models for physicochemical properties, pharmacokinetics, drug-likeness and medicinal chemistry friendliness, among which in-house proficient methods such as the BOILED-Egg, iLOGP and Bioavailability Radar. Easy efficient input and interpretation are ensured thanks to a user-friendly interface through the login-free website http://www.swissadme.ch. Specialists, but also nonexpert in cheminformatics or computational chemistry can predict rapidly key parameters for a collection of molecules to support their drug discovery endeavours.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
References
-
- Hay M., Thomas D. W., Craighead J. L., Economides C. & Rosenthal J. Clinical development success rates for investigational drugs. Nature Biotechnol. 32, 40–51 (2014). - PubMed
-
- Tian S. et al. The application of in silico drug-likeness predictions in pharmaceutical research. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 86, 2–10 (2015). - PubMed
-
- Lipinski C. A., Lombardo F., Dominy B. W. & Feeney P. J. Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 46, 3–26 (2001). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

