Capillary flow-driven microfluidic device with wettability gradient and sedimentation effects for blood plasma separation
- PMID: 28256564
- PMCID: PMC5335260
- DOI: 10.1038/srep43457
Capillary flow-driven microfluidic device with wettability gradient and sedimentation effects for blood plasma separation
Abstract
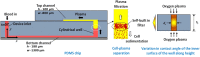
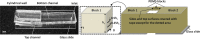
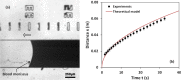
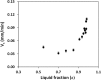
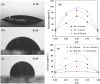
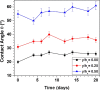
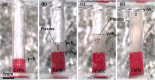
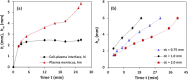
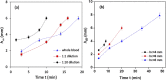
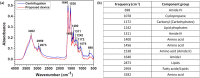
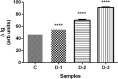
We report a capillary flow-driven microfluidic device for blood-plasma separation that comprises a cylindrical well between a pair of bottom and top channels. Exposure of the well to oxygen-plasma creates wettability gradient on its inner surface with its ends hydrophilic and middle portion hydrophobic. Due to capillary action, sample blood self-infuses into bottom channel and rises up the well. Separation of plasma occurs at the hydrophobic patch due to formation of a 'self-built-in filter' and sedimentation. Capillary velocity is predicted using a model and validated using experimental data. Sedimentation of RBCs is explained using modified Steinour's model and correlation between settling velocity and liquid concentration is found. Variation of contact angle on inner surface of the well is characterized and effects of well diameter and height and dilution ratio on plasma separation rate are investigated. With a well of 1.0 mm diameter and 4.0 mm height, 2.0 μl of plasma was obtained (from <10 μl whole blood) in 15 min with a purification efficiency of 99.9%. Detection of glucose was demonstrated with the plasma obtained. Wetting property of channels was maintained by storing in DI water under vacuum and performance of the device was found to be unaffected over three weeks.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Blok S. L., Engels G. E. & van Oeveren W. In vitro hemocompatibility testing: The importance of fresh blood. Biointerphases, 11, 029802-1-6 (2016). - PubMed
-
- Hou H. W. et al.. Microfluidic Devices for Blood Fractionation. Micromachines, 2, 319–343 (2011).
-
- Chandran K. B. Biofluid Mechanics-The human Circulation, CRC Press.
-
- Yeo L. Y., Friend J. R. & Arifin D. R. Electric tempest in a teacup: the tea leaf analogy to microfluidic blood plasma separation. Phys. Lett., 89, 103516-1-3 (2006).
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

