Transcatheter Heart Valve Selection and Permanent Pacemaker Implantation in Patients With Pre-Existent Right Bundle Branch Block
- PMID: 28258051
- PMCID: PMC5524025
- DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.116.005028
Transcatheter Heart Valve Selection and Permanent Pacemaker Implantation in Patients With Pre-Existent Right Bundle Branch Block
Abstract
Background: Right bundle branch block is an established predictor for new conduction disturbances and need for a permanent pacemaker (PPM) after transcatheter aortic valve replacement. The aim of the study was to evaluate the absolute rates of transcatheter aortic valve replacement related PPM implantations in patients with pre-existent right bundle branch block and categorize for different transcatheter heart valves.
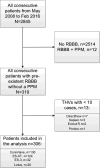
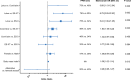
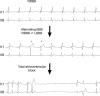
Methods and results: We pooled data on 306 transcatheter aortic valve replacement patients from 4 high-volume centers in Europe and selected those with right bundle branch block at baseline without a previously implanted PPM. Logistic regression was used to evaluate whether PPM rate differed among transcatheter heart valves after adjustment for confounders. Mean age was 83±7 years and 63% were male. Median Society of Thoracic Surgeons score was 6.3 (interquartile range, 4.1-10.2). The following transcatheter valve designs were used: Medtronic CoreValve (n=130; Medtronic, Minneapolis, MN); Edwards Sapien XT (ES-XT; n=124) and Edwards Sapien 3 (ES-3; n=32; Edwards Lifesciences, Irvine, CA); and Boston Scientific Lotus (n=20; Boston Scientific Corporation, Marlborough, MA). Overall permanent pacemaker implantation rate post-transcatheter aortic valve replacement was 41%, and per valve design: 75% with Lotus, 46% with CoreValve, 32% with ES-XT, and 34% with ES-3. The indication for PPM implantation was total atrioventricular block in 98% of the cases. Lotus was associated with a higher PPM rate than all other valves. PPM rate did not differ between ES-XT and ES-3. Ventricular paced rhythm at 30-day and 1-year follow-up was present in 81% at 89%, respectively.
Conclusions: Right bundle branch block at baseline is associated with a high incidence of PPM implantation for all transcatheter heart valves. PPM rate was highest for Lotus and lowest for ES-XT and ES-3. Pacemaker dependency remained high during follow-up.
Keywords: aortic stenosis; bundle‐branch block; pacemaker; predictors; right bundle branch block; transcatheter aortic valve implantation; transcatheter aortic valve replacement.
© 2017 The Authors. Published on behalf of the American Heart Association, Inc., by Wiley Blackwell.
Figures
References
-
- Reinohl J, Kaier K, Reinecke H, Schmoor C, Frankenstein L, Vach W, Cribier A, Beyersdorf F, Bode C, Zehender M. Effect of availability of transcatheter aortic‐valve replacement on clinical practice. N Engl J Med. 2015;373:2438–2447. - PubMed
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack M, Miller DC, Moses JW, Svensson LG, Tuzcu EM, Webb JG, Fontana GP, Makkar RR, Brown DL, Block PC, Guyton RA, Pichard AD, Bavaria JE, Herrmann HC, Douglas PS, Petersen JL, Akin JJ, Anderson WN, Wang D, Pocock S; Investigators PT . Transcatheter aortic‐valve implantation for aortic stenosis in patients who cannot undergo surgery. N Engl J Med. 2010;363:1597–1607. - PubMed
-
- Leon MB, Smith CR, Mack MJ, Makkar RR, Svensson LG, Kodali SK, Thourani VH, Tuzcu EM, Miller DC, Herrmann HC, Doshi D, Cohen DJ, Pichard AD, Kapadia S, Dewey T, Babaliaros V, Szeto WY, Williams MR, Kereiakes D, Zajarias A, Greason KL, Whisenant BK, Hodson RW, Moses JW, Trento A, Brown DL, Fearon WF, Pibarot P, Hahn RT, Jaber WA, Anderson WN, Alu MC, Webb JG; Investigators P . Transcatheter or surgical aortic‐valve replacement in intermediate‐risk patients. N Engl J Med. 2016;374:1609–1620. - PubMed
-
- Yamamoto M, Mouillet G, Oguri A, Gilard M, Laskar M, Eltchaninoff H, Fajadet J, Iung B, Donzeau‐Gouge P, Leprince P, Leuguerrier A, Prat A, Lievre M, Chevreul K, Dubois‐Rande JL, Teiger E; Investigators FR . Effect of body mass index on 30‐ and 365‐day complication and survival rates of transcatheter aortic valve implantation (from the French Aortic National Corevalve and Edwards 2 [FRANCE 2] Registry). Am J Cardiol. 2013;112:1932–1937. - PubMed
-
- van der Boon RM, Nuis RJ, Van Mieghem NM, Jordaens L, Rodes‐Cabau J, van Domburg RT, Serruys PW, Anderson RH, de Jaegere PP. New conduction abnormalities after TAVI–frequency and causes. Nat Rev Cardiol. 2012;9:454–463. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

