EphA4 Regulates Neuroblast and Astrocyte Organization in a Neurogenic Niche
- PMID: 28258169
- PMCID: PMC5373121
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3738-16.2017
EphA4 Regulates Neuroblast and Astrocyte Organization in a Neurogenic Niche
Abstract
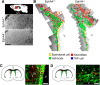
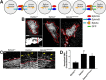
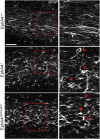
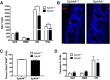
Significant migration cues are required to guide and contain newly generated rodent subventricular zone (SVZ) neuroblasts as they transit along the lateral ventricles and then through the anterior forebrain to their ultimate site of differentiation in the olfactory bulbs (OBs). These cues enforce strict neuroblast spatial boundaries within the dense astroglial meshwork of the SVZ and rostral migratory stream (RMS), yet are permissive to large-scale neuroblast migration. Therefore, the molecular mechanisms that define these cues and control dynamic interactions between migratory neuroblasts and surrounding astrocytes are of particular interest. We found that deletion of EphA4 and specifically ablation of EphA4 kinase activity resulted in misaligned neuroblasts and disorganized astrocytes in the RMS/SVZ, linking EphA4 forward signaling to SVZ and RMS spatial organization, orientation, and regulation. In addition, within a 3 week period, there was a significant reduction in the number of neuroblasts that reached the OB and integrated into the periglomerular layer, revealing a crucial role for EphA4 in facilitating efficient neuroblast migration to the OB. Single-cell analysis revealed that EPHA4 and its EFN binding partners are expressed by subpopulations of neuroblasts and astrocytes within the SVZ/RMS/OB system resulting in a cell-specific mosaic, suggesting complex EphA4 signaling involving both homotypic and heterotypic cell-cell interactions. Together, our studies reveal a novel molecular mechanism involving EphA4 signaling that functions in stem cell niche organization and ultimately neuroblast migration in the anterior forebrain.SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT The subventricular zone neurogenic stem cell niche generates highly migratory neuroblasts that transit the anterior forebrain along a defined pathway to the olfactory bulb. Postnatal and adult brain organization dictates strict adherence to a narrow migration corridor. Subventricular zone neuroblasts are aligned in tightly bundled chains within a meshwork of astrocytes; however, the cell-cell cues that organize this unique, cell-dense migration pathway are largely unknown. Our studies show that forward signaling through the EphA4 tyrosine kinase receptor, mediated by ephrins expressed by subpopulations of neuroblasts and astrocytes, is required for compact, directional organization of neuroblasts and astrocytes within the pathway and efficient transit of neuroblasts through the anterior forebrain to the olfactory bulb.
Keywords: astrocyte; migration; neuroblast; olfactory bulb; rostral migratory stream; subventricular zone.
Copyright © 2017 the authors 0270-6474/17/373331-11$15.00/0.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Fascin regulates the migration of subventricular zone-derived neuroblasts in the postnatal brain.J Neurosci. 2013 Jul 24;33(30):12171-85. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0653-13.2013. J Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 23884926 Free PMC article.
-
Astrocytic and vascular scaffolding for neuroblast migration in the rostral migratory stream.Curr Neurovasc Res. 2014;11(4):321-9. doi: 10.2174/1567202611666140903121253. Curr Neurovasc Res. 2014. PMID: 25182812
-
Relationship between Blood Vessels and Migration of Neuroblasts in the Olfactory Neurogenic Region of the Rodent Brain.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Oct 25;22(21):11506. doi: 10.3390/ijms222111506. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34768936 Free PMC article. Review.
-
β8 integrin is essential for neuroblast migration in the rostral migratory stream.Glia. 2011 Nov;59(11):1579-87. doi: 10.1002/glia.21199. Epub 2011 Jun 14. Glia. 2011. PMID: 21674628
-
Regulation of subventricular zone-derived cells migration in the adult brain.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015;853:1-21. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-16537-0_1. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2015. PMID: 25895704 Review.
Cited by
-
Microglia Maintain Homeostatic Conditions in the Developing Rostral Migratory Stream.eNeuro. 2023 Feb 8;10(2):ENEURO.0197-22.2023. doi: 10.1523/ENEURO.0197-22.2023. Print 2023 Feb. eNeuro. 2023. PMID: 36697258 Free PMC article.
-
Possible role of EphA4 and VEGFR2 interactions in neural stem and progenitor cell differentiation.Exp Ther Med. 2020 Mar;19(3):1789-1796. doi: 10.3892/etm.2020.8419. Epub 2020 Jan 3. Exp Ther Med. 2020. PMID: 32104234 Free PMC article.
-
Decreased Proliferation in the Neurogenic Niche, Disorganized Neuroblast Migration, and Increased Oligodendrogenesis in Adult Netrin-5-Deficient Mice.Front Neurosci. 2020 Nov 26;14:570974. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2020.570974. eCollection 2020. Front Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33324143 Free PMC article.
-
A mathematical model suggests collectivity and inconstancy enhance the efficiency of neuronal migration in the adult brain.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 Jun 5;21(6):e1013105. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1013105. eCollection 2025 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40471910 Free PMC article.
-
Blood vessels guide Schwann cell migration in the adult demyelinated CNS through Eph/ephrin signaling.Acta Neuropathol. 2019 Sep;138(3):457-476. doi: 10.1007/s00401-019-02011-1. Epub 2019 Apr 22. Acta Neuropathol. 2019. PMID: 31011859 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
