Assessing the Accuracy of the Modified Chinese Autism Spectrum Rating Scale and Social Responsiveness Scale for Screening Autism Spectrum Disorder in Chinese Children
- PMID: 28258510
- PMCID: PMC5360843
- DOI: 10.1007/s12264-017-0114-5
Assessing the Accuracy of the Modified Chinese Autism Spectrum Rating Scale and Social Responsiveness Scale for Screening Autism Spectrum Disorder in Chinese Children
Abstract
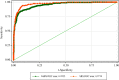
The reported prevalence of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) has been increasing rapidly in many parts of the world. However, data on its prevalence in China are largely missing. Here, we assessed the suitability of the modified Chinese version of a newly-developed ASD screening tool, the Modified Chinese Autism Spectrum Rating Scales (MC-ASRS) in screening for ASD in Chinese children aged 6-12 years, through comparison with the Social Responsiveness Scale (SRS) that has been widely used for ASD screening. We recruited the parents/caregivers of 1588 typically-developing children and 190 children with ASD aged 6-12 years to complete the MC-ASRS and SRS, and evaluated the validity of both scales in discriminating children with ASD from those developing typically. The results showed that MC-ASRS performed as well as SRS in sensitivity, specificity, and area-under-the-curve (both >0.95) in receiver operating characteristic analysis, with a fair false-negative rate. These results suggest that MC-ASRS is a promising tool for screening for children with ASD in the general Chinese population.
Keywords: Autism spectrum disorder; Modified Chinese Autism Spectrum Rating Scale; ROC analysis; Screening accuracy; Social Responsiveness Scale.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Reliability and validity of the translated Chinese version of Autism Spectrum Rating Scale (2-5 years).World J Pediatr. 2019 Feb;15(1):49-56. doi: 10.1007/s12519-018-0201-3. Epub 2018 Nov 16. World J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30446976
-
Performance of the Autism Spectrum Rating Scale and Social Responsiveness Scale in Identifying Autism Spectrum Disorder Among Cases of Intellectual Disability.Neurosci Bull. 2018 Dec;34(6):972-980. doi: 10.1007/s12264-018-0237-3. Epub 2018 May 28. Neurosci Bull. 2018. PMID: 29808467 Free PMC article.
-
Modifying the Autism Spectrum Rating Scale (6-18 years) to a Chinese Context: An Exploratory Factor Analysis.Neurosci Bull. 2017 Apr;33(2):175-182. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0104-7. Epub 2017 Feb 25. Neurosci Bull. 2017. PMID: 28238114 Free PMC article.
-
Screening accuracy of Level 2 autism spectrum disorder rating scales. A review of selected instruments.Autism. 2010 Jul;14(4):263-84. doi: 10.1177/1362361309348071. Autism. 2010. PMID: 20591956 Review.
-
A systematic review of screening tools in non-young children and adults for autism spectrum disorder.Res Dev Disabil. 2018 Sep;80:1-12. doi: 10.1016/j.ridd.2018.05.017. Epub 2018 Jun 4. Res Dev Disabil. 2018. PMID: 29879612
Cited by
-
Towards the Framework of Understanding Autism Spectrum Disorders.Neurosci Bull. 2019 Nov 9;35(6):1110-2. doi: 10.1007/s12264-019-00443-z. Online ahead of print. Neurosci Bull. 2019. PMID: 31707712 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Psychometric properties of the Chinese Parent Version of the Autism Spectrum Rating Scale: Rasch analysis.Autism. 2021 Oct;25(7):1872-1884. doi: 10.1177/13623613211004054. Epub 2021 Apr 12. Autism. 2021. PMID: 33845648 Free PMC article.
-
Reliability and validity of the translated Chinese version of Autism Spectrum Rating Scale (2-5 years).World J Pediatr. 2019 Feb;15(1):49-56. doi: 10.1007/s12519-018-0201-3. Epub 2018 Nov 16. World J Pediatr. 2019. PMID: 30446976
-
Cerebral blood flow characteristics of drug-naïve attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder with social impairment: Evidence for region-symptom specificity.Front Neurosci. 2023 Mar 21;17:1149703. doi: 10.3389/fnins.2023.1149703. eCollection 2023. Front Neurosci. 2023. PMID: 37025372 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Research Progress in Autism Spectrum Disorder.Neurosci Bull. 2017 Apr;33(2):125-129. doi: 10.1007/s12264-017-0117-2. Epub 2017 Mar 11. Neurosci Bull. 2017. PMID: 28285467 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders. 4th ed revised. Washington, DC: American Psychiatric Association, 2000.
-
- American Psychiatric Association. Neurodevelopmental disorders. Autism spectrum disorder. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders (5th ed.) 2013.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical