TAM receptor tyrosine kinases as emerging targets of innate immune checkpoint blockade for cancer therapy
- PMID: 28258690
- PMCID: PMC5381815
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.12522
TAM receptor tyrosine kinases as emerging targets of innate immune checkpoint blockade for cancer therapy
Abstract
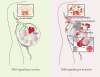
Cancer immunotherapy utilizing T-cell checkpoint inhibitors has shown tremendous clinical success. Yet, this mode of treatment is effective in only a subset of patients. Unresponsive patients tend to have non-T-cell-inflamed tumors that lack markers associated with the activation of adaptive anti-tumor immune responses. Notably, elimination of cancer cells by T cells is critically dependent on the optimal activity of innate immune cells. Therefore, identifying new targets that regulate innate immune cell function and promote the engagement of adaptive tumoricidal responses is likely to lead to the development of improved therapies against cancer. Here, we review the TAM receptor tyrosine kinases-TYRO3, AXL, and MERTK-as an emerging class of innate immune checkpoints that participate in key steps of anti-tumoral immunity. Namely, TAM-mediated efferocytosis, negative regulation of dendritic cell activity, and dysregulated production of chemokines collectively favor the escape of malignant cells. Hence, disabling TAM signaling may promote engagement of adaptive immunity and complement T-cell checkpoint blockade.
Keywords: AXL; MERTK; TYRO3; innate immune checkpoints.
© 2017 John Wiley & Sons A/S. Published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors disclose that there is a potential conflict of interest as C.V.R. is a shareholder of Kolltan Pharmaceuticals and a member of the science advisory board at Surface Oncology.
Figures


References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

