Gene body DNA methylation in plants
- PMID: 28258985
- PMCID: PMC5413422
- DOI: 10.1016/j.pbi.2016.12.007
Gene body DNA methylation in plants
Abstract
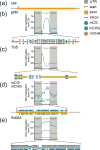
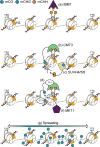
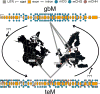
The type, amount, and location of DNA methylation within a gene provides pivotal information on the enzymatic pathway by which it was achieved and its functional consequences. In plants (angiosperms specifically), gene body methylation (gbM) refers to genes with an enrichment of CG DNA methylation within the transcribed regions and depletion at the transcriptional start and termination sites. GbM genes often compose the bulk of methylated genes within angiosperm genomes and are enriched for housekeeping functions. Contrary to the transcriptionally repressive effects of other chromatin modifications within gene bodies, gbM genes are constitutively expressed. GbM has intrigued researchers since its discovery, and much effort has been placed on identifying its functional role. Here, we highlight the recent findings on the evolutionary origin and molecular mechanism of gbM and synthesize studies describing the possible roles for this enigmatic epigenetic phenotype.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Zilberman D, Gehring M, Tran RK, Ballinger T, Henikoff S. Genome-wide analysis of Arabidopsis thaliana DNA methylation uncovers an interdependence between methylation and transcription. Nat Genet. 2006;39:61–69. One of the earlier studies investigating DNA methylation from a genomic perspective and perturbations to DNA methylation caused by met1. - PubMed
-
- Feng S, Cokus SJ, Zhang X, Chen PY, Bostick M, Goll MG, Hetzel J, Jain J, Strauss SH, Halpern ME, Ukomadu C, Sadler KC, Pradhan S, Pellegrini M, Jacobsen SE. Conservation and divergence of methylation patterning in plants and animals. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107:8689–8694. A comparative study illustrating the similarities and differences of DNA methylation between eight diverse plant and animal, and the prevalence of DNA methylation within genes. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zemach A, McDaniel IE, Silva P, Zilberman D. Genome-wide evolutionary analysis of eukaryotic DNA methylation. Science. 2010;328:916–919. DNA methylation analysis of 17 eukaryotic genomes. This study substantially expanded taxonomic sampling regarding DNA methylomes, and provided evidence for conservation of DNA methylation within gene bodies and H2A.Z. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

