Glutamate released in the preoptic area during sexual behavior controls local estrogen synthesis in male quail
- PMID: 28259043
- PMCID: PMC5432736
- DOI: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.02.002
Glutamate released in the preoptic area during sexual behavior controls local estrogen synthesis in male quail
Abstract
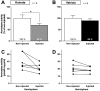
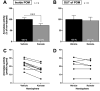
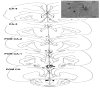
Estrogens are known to act rapidly, probably via membrane estrogen receptors, to induce fast effects on physiological and behavioral processes. Engaging in some of these behaviors, such as sexual behavior, results in an acute modulation of the production of estrogens in the brain by regulating the efficiency of the estrogen synthase enzyme, aromatase. We recently demonstrated that aromatase activity (AA) in the male quail brain is rapidly inhibited in discrete brain regions including the medial preoptic nucleus (POM) following exposure to a female. Evidence from in vitro studies point to glutamate release as one of the mechanisms controlling these rapid regulations of the aromatase enzyme. Here, we show that (a) the acute injection of the glutamatergic agonist kainate into the POM of anesthetized male quail inhibits AA and (b) glutamate is released in the POM during copulation. These results provide the first set of in vivo data demonstrating a role for glutamate release in the rapid control of AA in the context of sexual behavior.
Keywords: Aromatase; Estrogen synthesis; Glutamate; Japanese quail; Sexual behavior.
Copyright © 2017 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures

References
-
- Adkins EK, Adler NT. Hormonal control of behavior in the Japanese quail. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1972;81:27–36. - PubMed
-
- Aste N, Panzica GC, Aimar P, Viglietti-Panzica C, Harada N, Foidart A, Balthazart J. Morphometric studies demonstrate that aromatase-immunoreactive cells are the main target of androgens and estrogens in the quail medial preoptic nucleus. Exp Brain Res. 1994;101:241–252. - PubMed
-
- Azcoitia I, Yague JG, Garcia-Segura LM. Estradiol synthesis within the human brain. Neuroscience. 2011;191:139–147. - PubMed
-
- Baillien M, Balthazart J. A direct dopaminergic control of aromatase activity in the quail preoptic area. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol. 1997;63:99–113. - PubMed
-
- Balthazart J, Absil P, Gerard M, Appeltants D, Ball GF. Appetitive and consummatory male sexual behavior in Japanese quail are differentially regulated by subregions of the preoptic medial nucleus. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience. 1998;18:6512–6527. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

