N-butanol extracts of Morinda citrifolia suppress advanced glycation end products (AGE)-induced inflammatory reactions in endothelial cells through its anti-oxidative properties
- PMID: 28259164
- PMCID: PMC5336679
- DOI: 10.1186/s12906-017-1641-3
N-butanol extracts of Morinda citrifolia suppress advanced glycation end products (AGE)-induced inflammatory reactions in endothelial cells through its anti-oxidative properties
Abstract
Background: Advanced glycation end products (AGEs), senescent macroprotein derivatives formed during a normal aging process and acceleratedly under diabetic conditions, play a role in atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease. AGEs cause endothelial cell (EC) damage, an initial trigger for atherosclerosis through the interaction with a receptor for AGEs (RAGE). We have previously shown that n-butanol extracts of Morinda citrifolia (noni), a plant belonging to the family Rubiaceae, block the binding of AGEs to RAGE in vitro. In this study, we examined the effects of n-butanol extracts of noni on reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation and inflammatory reactions on AGE-exposed human umbilical vein ECs (HUVECs).
Methods: HUVECs were treated with 100 μg/ml AGE-bovine serum albumin (AGE-BSA) or non-glycated BSA in the presence or absence of 670 ng/ml n-butanol extracts of noni for 4 h. Then ROS generation and inflammatory and gene expression in HUVECs were evaluated by dihydroethidium staining and real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction analyses, respectively. THP-1 cell adhesion to HUVECs was measured after 2-day incubation of AGE-BSA or BSA in the presence or absence of 670 ng/ml n-butanol extracts of noni.
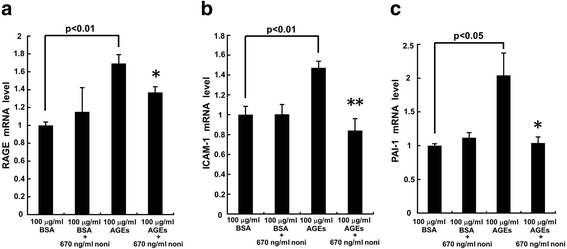
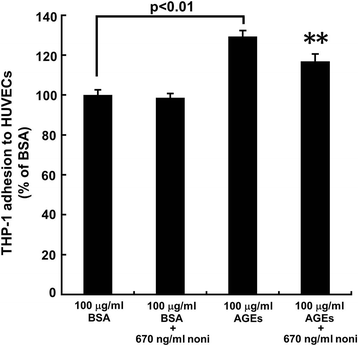
Results: N-butanol extracts of noni at 670 ng/ml significantly inhibited the AGE-induced ROS generation and RAGE, intercellular adhesion molecule-1 and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 gene expressions in HUVECs. AGEs significantly increased monocytic THP-1 cell adhesion to HUVECs, which was also prevented by 670 ng/ml n-butanol extracts of noni.
Conclusions: The present study demonstrated for the first time that N-butanol extracts of noni could suppress the AGE-induced inflammatory reactions in HUVECs through its anti-oxidative properties via blocking of the interaction of AGEs with RAGE. Inhibition of the AGE-RAGE axis by n-butanol extracts of noni may be a novel nutraceutical strategy for the treatment of cardiovascular disease.
Keywords: AGEs; Atherosclerosis; Oxidative stress; RAGE.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Glyceraldehyde-derived pyridinium (GLAP) evokes oxidative stress and inflammatory and thrombogenic reactions in endothelial cells via the interaction with RAGE.Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015 Jan 8;14:1. doi: 10.1186/s12933-014-0162-3. Cardiovasc Diabetol. 2015. PMID: 25582325 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitory effect of GSPE on RAGE expression induced by advanced glycation end products in endothelial cells.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007 Oct;50(4):434-40. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e3181342bfa. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 18049312
-
Blockade by phosphorothioate aptamers of advanced glycation end products-induced damage in cultured pericytes and endothelial cells.Microvasc Res. 2013 Nov;90:64-70. doi: 10.1016/j.mvr.2013.08.010. Epub 2013 Sep 5. Microvasc Res. 2013. PMID: 24012635
-
Morinda citrifolia (Noni): a literature review and recent advances in Noni research.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002 Dec;23(12):1127-41. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2002. PMID: 12466051 Review.
-
Do the health claims made for Morinda citrifolia (Noni) harmonize with current scientific knowledge and evaluation of its biological effects.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(8):4495-9. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.8.4495. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 24083691 Review.
Cited by
-
Vascular Protective Effects of Malus toringoides (Rehd.) Hughes Extracts and their Mechanism in Diabetic Rats and HUVECs.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 19;2022:4348435. doi: 10.1155/2022/4348435. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36310615 Free PMC article.
-
AGE-RAGE Axis Stimulates Oxidized LDL Uptake into Macrophages through Cyclin-Dependent Kinase 5-CD36 Pathway via Oxidative Stress Generation.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Dec 4;21(23):9263. doi: 10.3390/ijms21239263. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33291667 Free PMC article.
-
1α,25-dihydroxyvitamin D3 promotes osseointegration of titanium implant via downregulating AGEs/RAGE pathway in T2DM.Endocr Connect. 2018 Nov;7(11):1186-1195. doi: 10.1530/EC-18-0241. Endocr Connect. 2018. PMID: 30352411 Free PMC article.
-
Radical oxygen species: an important breakthrough point for botanical drugs to regulate oxidative stress and treat the disorder of glycolipid metabolism.Front Pharmacol. 2023 May 12;14:1166178. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1166178. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37251336 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the therapeutic mechanisms of Coptidis Rhizoma in gastric precancerous lesions: a network pharmacology approach.Discov Oncol. 2024 Jun 5;15(1):211. doi: 10.1007/s12672-024-01070-5. Discov Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38837097 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

