Development of a common carp (Cyprinus carpio) pregnane X receptor (cPXR) transactivation reporter assay and its activation by azole fungicides and pharmaceutical chemicals
- PMID: 28259787
- PMCID: PMC5484788
- DOI: 10.1016/j.tiv.2017.02.023
Development of a common carp (Cyprinus carpio) pregnane X receptor (cPXR) transactivation reporter assay and its activation by azole fungicides and pharmaceutical chemicals
Abstract
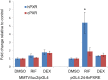
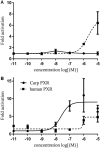
In mammals, the pregnane X receptor (PXR) is a transcription factor with a key role in regulating expression of several genes involved in drug biotransformation. PXR is present in fish and some genes known to be under its control can be up-regulated by mammalian PXR ligands. Despite this, direct involvement of PXR in drug biotransformation in fish has yet to be established. Here, the full length PXR sequence was cloned from carp (Cyprinus carpio) and used in a luciferase reporter assay to elucidate its role in xenobiotic metabolism in fish. A reporter assay for human PXR (hPXR) was also established to compare transactivation between human and carp (cPXR) isoforms. Rifampicin activated hPXR as expected, but not cPXR. Conversely, clotrimazole (CTZ) activated both isoforms and was more potent on cPXR, with an EC50 within the range of concentrations of CTZ measured in the aquatic environment. Responses to other azoles tested were similar between both isoforms. A range of pharmaceuticals tested either failed to activate, or were very weakly active, on the cPXR or hPXR. Overall, these results indicate that the cPXR may differ from the hPXR in its responses and/or sensitivity to induction by different environmental chemicals, with implications for risk assessment because of species differences.
Keywords: Azole fungicides; Common carp; Human; Pharmaceuticals; Pregnane X receptor; Transient transactivation assay.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Ltd.. All rights reserved.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Functional characterization of four naturally occurring variants of human pregnane X receptor (PXR): one variant causes dramatic loss of both DNA binding activity and the transactivation of the CYP3A4 promoter/enhancer region.Drug Metab Dispos. 2004 Jan;32(1):149-54. doi: 10.1124/dmd.32.1.149. Drug Metab Dispos. 2004. PMID: 14709632
-
Bioavailability of the imidazole antifungal agent clotrimazole and its effects on key biotransformation genes in the common carp (Cyprinus carpio).Aquat Toxicol. 2014 Jul;152:57-65. doi: 10.1016/j.aquatox.2014.03.016. Epub 2014 Mar 29. Aquat Toxicol. 2014. PMID: 24727216
-
Environmental phthalate monoesters activate pregnane X receptor-mediated transcription.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004 Sep 15;199(3):266-74. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2003.11.028. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2004. PMID: 15364542
-
Endocrine disruption by azole fungicides in fish: A review of the evidence.Sci Total Environ. 2022 May 20;822:153412. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153412. Epub 2022 Jan 25. Sci Total Environ. 2022. PMID: 35090921 Review.
-
A comprehensive review on environmental toxicity of azole compounds to fish.Chemosphere. 2021 Jan;262:128335. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.128335. Epub 2020 Sep 14. Chemosphere. 2021. PMID: 33182121 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of nuclear pregnane X receptor in Cu-induced lipid metabolism and xenobiotic responses in largemouth bass (Micropterus salmoides).Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jul 28;13:950985. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.950985. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35966089 Free PMC article.
-
The Connection of Azole Fungicides with Xeno-Sensing Nuclear Receptors, Drug Metabolism and Hepatotoxicity.Cells. 2020 May 11;9(5):1192. doi: 10.3390/cells9051192. Cells. 2020. PMID: 32403288 Free PMC article. Review.
-
KnowTox: pipeline and case study for confident prediction of potential toxic effects of compounds in early phases of development.J Cheminform. 2020 Apr 14;12(1):24. doi: 10.1186/s13321-020-00422-x. J Cheminform. 2020. PMID: 33431007 Free PMC article.
-
A Comparative Study of Human and Zebrafish Pregnane X Receptor Activities of Pesticides and Steroids Using In Vitro Reporter Gene Assays.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 May 18;12:665521. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.665521. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34084152 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W., Lipman D.J. Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 1990;215:403–410. - PubMed
-
- Aus der Beek T., Weber F.-A., Bergmann A., Hickmann S., Ebert I., Hein A., Küster A. Pharmaceuticals in the environment—global occurrences and perspectives. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2016;35:823–835. - PubMed
-
- Bainy A.C.D., Stegeman J.J. Cloning and identification of a full length pregnane X receptor and expression in vivo in zebrafish (Danio rerio) Mar. Environ. Res. 2004;58:133–134.
-
- Bainy A.C.D., Kubota A., Goldstone J.V., Lille-Langøy R., Karchner S.I., Celander M.C., Hahn M.E., Goksøyr A., Stegeman J.J. Functional characterization of a full length pregnane X receptor, expression in vivo, and identification of PXR alleles, in zebrafish (Danio rerio) Aquat. Toxicol. 2013;142:447–457. - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

