Effects of R type and S type ginsenoside Rg3 on DNA methylation in human hepatocarcinoma cells
- PMID: 28260016
- PMCID: PMC5364960
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6255
Effects of R type and S type ginsenoside Rg3 on DNA methylation in human hepatocarcinoma cells
Abstract
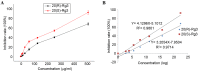
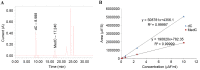
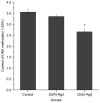
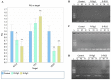
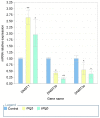
Ginsenoside Rg3, a bioactive constituent isolated from Panax ginseng, exhibits antitumorigenic, antioxidative, antiangiogenic, neuroprotective and other biological activities are associated with the regulation of multiple genes. DNA methylation patterns, particularly those in the promoter region, affect gene expression, and DNA methylation is catalyzed by DNA methylases. However, whether ginsenoside Rg3 affects DNA methylation is unknown. High performance liquid chromatography assay, MspI/HpaII polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR were performed to assess DNA methylation. It was demonstrated that 20(S)‑ginsenoside Rg3 treatment resulted in increased inhibition of cell growth, compared with treatment with 20(R)‑ginsenoside Rg3 in the human HepG2 hepatocarcinoma cell line. It was additionally revealed that treatment with 20(S)‑ginsenoside Rg3 reduced global genomic DNA methylation, altered cystosine methylation of the promoter regions of P53, B cell lymphoma 2 and vascular endothelial growth factor, and downregulated the expression of DNA methyltransferase (DNMT) 3a and DNMT3b more than treatment with 20(R)‑ginsenoside Rg3 in HepG2 cells. These results revealed that the modulation of DNA methylation may be important in the pharmaceutical activities of ginsenoside Rg3.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Ginsenoside 20(S)-Rg3 Inhibits the Warburg Effect Via Modulating DNMT3A/ MiR-532-3p/HK2 Pathway in Ovarian Cancer Cells.Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018;45(6):2548-2559. doi: 10.1159/000488273. Epub 2018 Mar 16. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29558748
-
Antitumor effects of ginsenoside Rg3 on human hepatocellular carcinoma cells.Mol Med Rep. 2012 May;5(5):1295-8. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2012.808. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Mol Med Rep. 2012. PMID: 22366885
-
Ginsenoside Rg3 induces apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells via the activation of Bcl-2-associated X protein.Mol Med Rep. 2015 Sep;12(3):3557-3562. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.3802. Epub 2015 May 19. Mol Med Rep. 2015. PMID: 25998024
-
Anticancer effects of ginsenoside Rg3 (Review).Int J Mol Med. 2017 Mar;39(3):507-518. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2857. Epub 2017 Jan 13. Int J Mol Med. 2017. PMID: 28098857 Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3: A Review of its Anticancer Mechanisms and Potential Therapeutic Applications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2024;24(10):869-884. doi: 10.2174/0115680266283661240226052054. Curr Top Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38441023 Review.
Cited by
-
Saponins of ginseng products: a review of their transformation in processing.Front Pharmacol. 2023 Apr 28;14:1177819. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1177819. eCollection 2023. Front Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37188270 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of Long Non-Coding RNAs by Plant Secondary Metabolites: A Novel Anticancer Therapeutic Approach.Cancers (Basel). 2021 Mar 13;13(6):1274. doi: 10.3390/cancers13061274. Cancers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33805687 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ginsenoside Rg3: Potential Molecular Targets and Therapeutic Indication in Metastatic Breast Cancer.Medicines (Basel). 2019 Jan 23;6(1):17. doi: 10.3390/medicines6010017. Medicines (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30678106 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Studies of Chinese Herbal Medicine: Pleiotropic Role of DNA Methylation.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 7;12:790321. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.790321. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34950039 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The pharmacological role of Ginsenoside Rg3 in liver diseases: A review on molecular mechanisms.J Ginseng Res. 2024 Mar;48(2):129-139. doi: 10.1016/j.jgr.2023.11.004. Epub 2023 Nov 15. J Ginseng Res. 2024. PMID: 38465219 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Luo Y, Zhang P, Zeng HQ, Lou SF, Wang DX. Ginsenoside Rg3 induces apoptosis in human multiple myeloma cells via the activation of Bcl-2-associated X protein. Mol Med Rep. 2015;12:3557–3562. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

