Slit2 suppresses endothelial cell proliferation and migration by inhibiting the VEGF-Notch signaling pathway
- PMID: 28260032
- PMCID: PMC5364956
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6240
Slit2 suppresses endothelial cell proliferation and migration by inhibiting the VEGF-Notch signaling pathway
Retraction in
-
[Retracted] Slit2 suppresses endothelial cell proliferation and migration by inhibiting the VEGF‑Notch signaling pathway.Mol Med Rep. 2025 Aug;32(2):207. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2025.13572. Epub 2025 May 26. Mol Med Rep. 2025. PMID: 40417874 Free PMC article.
Abstract
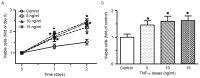
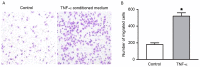
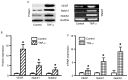
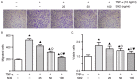
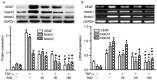
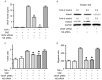
Slit homolog 2 (Slit2) is distributed in various tissues and participates in numerous cellular processes; however, the role of Slit2 in the regulation of angiogenesis remains controversial, since it has previously been reported to exert proangiogenic and antiangiogenic activities. The present study aimed to investigate the effects of Slit2 on vascular endothelial cell proliferation and migration in vitro, and to reveal the possible underlying signaling pathway. Aortic endothelial cells were isolated from Sprague Dawley rats and cultured. Cell proliferation assay, cell migration assay, immunocytochemistry and small interfering RNA transfection were subsequently performed. The results demonstrated that exogenous Slit2 administration markedly suppressed TNF‑α‑induced endothelial cell proliferation and migration in vitro. In addition, TNF‑α application upregulated the protein expression levels of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) and Notch in RAECs, whereas Slit2 administration downregulated VEGF and Notch expression in RAECs cultured in TNF‑α conditioned medium. Further studies indicated that knockdown of VEGF suppressed the effects of TNF‑α on the induction of RAEC proliferation and migration. VEGF knockdown‑induced inhibition of RAEC proliferation and migration in TNF‑α conditioned medium was also achieved without Slit2 administration. Furthermore, VEGF knockdown markedly decreased Notch1 and Notch2 expression. These results indicated that Slit2 suppresses TNF‑α‑induced vascular endothelial cell proliferation and migration in vitro by inhibiting the VEGF‑Notch signaling pathway. Therefore, Slit2 may inhibit the proliferation and migration of endothelial cells during vascular development.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The role of SLIT-ROBO signaling in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and retinal pigment epithelial cells.Mol Vis. 2011;17:1526-36. Epub 2011 Jun 8. Mol Vis. 2011. PMID: 21686327 Free PMC article.
-
[Myocardial Slit2/Robo4 expression and impact of exogenous Slit2 on proliferation and migration of cardiac microvascular endothelial cells].Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2013 Dec;41(12):1034-9. Zhonghua Xin Xue Guan Bing Za Zhi. 2013. PMID: 24524607 Chinese.
-
Slit2/Robo1 signaling is involved in angiogenesis of glomerular endothelial cells exposed to a diabetic-like environment.Angiogenesis. 2018 May;21(2):237-249. doi: 10.1007/s10456-017-9592-3. Epub 2018 Jan 3. Angiogenesis. 2018. PMID: 29299781
-
Elevated Slit2 Activity Impairs VEGF-Induced Angiogenesis and Tumor Neovascularization in EphA2-Deficient Endothelium.Mol Cancer Res. 2015 Mar;13(3):524-37. doi: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0142. Epub 2014 Dec 12. Mol Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 25504371 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of endothelial cell differentiation and arterial specification by VEGF and Notch signaling.Anat Sci Int. 2009 Sep;84(3):95-101. doi: 10.1007/s12565-009-0026-1. Epub 2009 Mar 4. Anat Sci Int. 2009. PMID: 19259767 Review.
Cited by
-
ALDOA protects cardiomyocytes against H/R-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress by regulating the VEGF/Notch 1/Jagged 1 pathway.Mol Cell Biochem. 2021 Feb;476(2):775-783. doi: 10.1007/s11010-020-03943-z. Epub 2020 Oct 21. Mol Cell Biochem. 2021. PMID: 33089381
-
MCAM/MUC18/CD146 as a Multifaceted Warning Marker of Melanoma Progression in Liquid Biopsy.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Nov 17;22(22):12416. doi: 10.3390/ijms222212416. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34830300 Free PMC article.
-
Uric acid promotes oxidative stress and enhances vascular endothelial cell apoptosis in rats with middle cerebral artery occlusion.Biosci Rep. 2018 May 15;38(3):BSR20170939. doi: 10.1042/BSR20170939. Print 2018 May 15. Biosci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29097484 Free PMC article.
-
Methylome analysis of endothelial cells suggests new insights on sporadic brain arteriovenous malformation.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 30;10(15):e35126. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e35126. eCollection 2024 Aug 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39170526 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Remodeling of Ductus Arteriosus: Looking beyond the Prostaglandin Pathway.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Mar 22;22(6):3238. doi: 10.3390/ijms22063238. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 33810164 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

