A herbal formula, SYKT, reverses doxorubicin‑induced myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity by inhibiting ROS‑mediated apoptosis
- PMID: 28260045
- PMCID: PMC5364961
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6272
A herbal formula, SYKT, reverses doxorubicin‑induced myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity by inhibiting ROS‑mediated apoptosis
Abstract
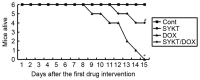
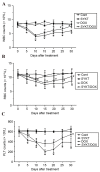
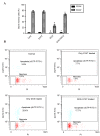
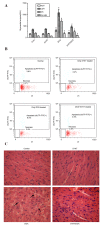
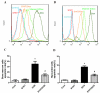
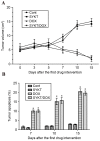
Doxorubicin (DOX) is an antineoplastic drug widely used for the treatment of various types of cancer; however, it can induce severe side effects, such as myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity. Sanyang Xuedai (SYKT) is a natural medicine originating from an ancient prescription of the Dai nationality in Southwest China. With eight Chinese herbal medicines, including sanguis draconis, radix et rhizoma notoginseng, radix et rhizoma glycyrrhizae and radix angelicae sinensis as the primary ingredients, SYKT has been reported to possess numerous biological functions. The present study investigated whether SYKT can confer protection against DOX‑induced myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity, and explored the potential mechanism involved. Mice were treated with DOX, SYKT or a combination of the two; hematopoietic functions were assessed by measuring the number of peripheral blood cells, cluster of differentiation CD34+/CD44+ bone marrow cells and apoptotic cells. Myocardial enzymes, including aspartate aminotransferase, lactate dehydrogenase, creatine kinase (CK) and its isoform CK‑MB, were assessed using a biochemical analyzer. The apoptotic rate of cardiomyocytes was assessed using flow cytometry. Histopathological analysis was conducted using hematoxylin‑eosin staining. Intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS) production was evaluated using a dichlorofluorescein intensity assay. The mice treated with DOX exhibited a reduced survival rate, reduced peripheral blood and CD34+/CD44+ cell counts, elevated myocardial enzymes and apoptotic indices in bone marrow cells and cardiomyocytes, all of which were effectively prevented by SYKT co‑administration. Furthermore, bone marrow cells and myocytes from mice treated with DOX demonstrated increased dichlorofluorescein intensity, which was attenuated by SYKT. Notably, SYKT did not interfere with the effects of DOX on tumor volume or the induction of tumor cell apoptosis in tumor‑bearing mice. The present study indicated that SYKT may counteract DOX‑induced myelosuppression and cardiotoxicity through inhibiting ROS‑mediated apoptosis. These findings suggested that SYKT may have potential as a means to counteract the potentially fatal hematopoietic and cardiac complications associated with DOX treatment.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Adiponectin agonist ADP355 ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by decreasing cardiomyocyte apoptosis and oxidative stress.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020 Dec 10;533(3):304-312. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.09.035. Epub 2020 Sep 18. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020. PMID: 32958254
-
SYKT Alleviates Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity via Modulating ROS-Mediated p53 and MAPK Signal Pathways.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Aug 26;2018:2581031. doi: 10.1155/2018/2581031. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30224925 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity and genotoxicity by an indole-based natural compound 3,3'-diindolylmethane (DIM) through activation of Nrf2/ARE signaling pathways and inhibiting apoptosis.Free Radic Res. 2017 Oct;51(9-10):812-827. doi: 10.1080/10715762.2017.1381694. Epub 2017 Oct 12. Free Radic Res. 2017. PMID: 28922986
-
Cardioprotective mechanisms of phytochemicals against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity.Biomed Pharmacother. 2017 Jun;90:935-946. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.033. Epub 2017 Apr 26. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017. PMID: 28460429 Review.
-
The role of toll-like receptors in myocardial toxicity induced by doxorubicin.Immunol Lett. 2020 Jan;217:56-64. doi: 10.1016/j.imlet.2019.11.001. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Immunol Lett. 2020. PMID: 31707054 Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancement of the therapeutic efficacy of the MAP regimen using thiamine pyrophosphate-decorated albumin nanoclusters in osteosarcoma treatment.Bioeng Transl Med. 2022 Dec 26;8(6):e10472. doi: 10.1002/btm2.10472. eCollection 2023 Nov. Bioeng Transl Med. 2022. PMID: 38023714 Free PMC article.
-
The Application of Ethnomedicine in Modulating Megakaryocyte Differentiation and Platelet Counts.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Feb 5;24(4):3168. doi: 10.3390/ijms24043168. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36834579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Herbo-Mineral Medicine, Cardiogrit Gold, Exhibits Protective Effects in Caenorhabditis elegans Model of Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiotoxicity.J Toxicol. 2025 Jul 28;2025:4609428. doi: 10.1155/jt/4609428. eCollection 2025. J Toxicol. 2025. PMID: 40761538 Free PMC article.
-
A medicinal and edible formula YH0618 ameliorates the toxicity induced by Doxorubicin via regulating the expression of Bax/Bcl-2 and FOXO4.J Cancer. 2019 Jun 9;10(16):3665-3677. doi: 10.7150/jca.32754. eCollection 2019. J Cancer. 2019. PMID: 31333784 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of SXN in the Treatment of Iron Deficiency Anemia: A Phase IV Clinical Trial.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019 Mar 3;2019:8796234. doi: 10.1155/2019/8796234. eCollection 2019. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2019. PMID: 30941201 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swain SM. Doxorubicin-induced cardiomyopathy. N Engl J Med. 1999;340:654. - PubMed
-
- Vadhan-Raj S, Patel S, Bueso-Ramos C, Folloder J, Papadopolous N, Burgess A, Broemeling LD, Broxmeyer HE, Benjamin RS. Importance of predosing of recombinant human thrombopoietin to reduce chemotherapy-induced early thrombocytopenia. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:3158–3167. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.08.003. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

