Automatic and Precise Localization and Cortical Labeling of Subdural and Depth Intracranial Electrodes
- PMID: 28261083
- PMCID: PMC5314105
- DOI: 10.3389/fninf.2017.00010
Automatic and Precise Localization and Cortical Labeling of Subdural and Depth Intracranial Electrodes
Abstract
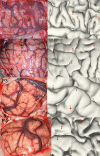
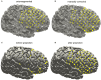
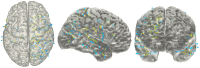
Object: Subdural or deep intracerebral electrodes are essential in order to precisely localize epileptic zone in patients with medically intractable epilepsy. Precise localization of the implanted electrodes is critical to clinical diagnosing and treatment as well as for scientific studies. In this study, we sought to automatically and precisely extract intracranial electrodes using pre-operative MRI and post-operative CT images. Method: The subdural and depth intracranial electrodes were readily detected using clustering-based segmentation. Depth electrodes were tracked by fitting a quadratic curve to account for potential bending during the neurosurgery. The identified electrodes can be manipulated using a graphic interface and labeled to cortical areas in individual native space based on anatomical parcellation and displayed in the volume and surface space. Results: The electrodes' localizations were validated with high precision. The electrode coordinates were normalized to a standard space. Moreover, the probabilistic value being to a specific area or a functional network was provided. Conclusions: We developed an integrative toolbox to reconstruct and label the intracranial electrodes implanted in the patients with medically intractable epilepsy. This toolbox provided a convenient way to allow inter-subject comparisons and relation of intracranial EEG findings to the larger body of neuroimaging literature.
Keywords: ECoG; SEEG; electrode localization; intracranial EEG; intractable epilepsy.
Figures





References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

