Curcumin Alleviates oxLDL Induced MMP-9 and EMMPRIN Expression through the Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in Macrophages
- PMID: 28261097
- PMCID: PMC5306337
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00062
Curcumin Alleviates oxLDL Induced MMP-9 and EMMPRIN Expression through the Inhibition of NF-κB and MAPK Pathways in Macrophages
Abstract
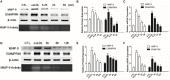
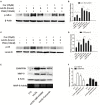
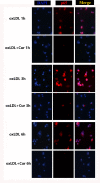
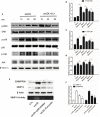
Rupture of vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques is the leading cause of acute myocardial infarction (AMI) and unstable angina pectoris (UA). However, it still lacks an effective therapy to stabilize the vulnerable atherosclerotic plaques. Numerous reports have shown that upregulation of MMP-9 (matrix metalloproteinase-9) and EMMPRIN (extracellular matrix metalloproteinase inducer) in macrophages is involved in the progression and development of vulnerable plaques. Here we evaluated the impact of curcumin on the expression of MMP-9 and EMMPRIN in macrophages. Macrophages were pretreated with curcumin or specific inhibitors (p38 MAPK inhibitor, NF-κB p65 inhibitor) for 1 h, then cells were cultured with oxLDL for indicated time. Real-time PCR and Western blot analysis were used to evaluate the expression of mRNA and proteins. Translocation of NF-κB p65 was detected by using laser confocal microscopy. Here we showed that curcumin attenuated the MMP-9 and EMMPRIN expression in oxLDL stimulated macrophages. Further studies revealed that curcumin inhibited oxLDL induced NF-κB activation and p38 MAPK phosphorylation. These findings illustrated that curcumin can inhibit the expression of EMMPRIN and MMP-9 in oxLDL stimulated macrophages through down regulation of NF-κB and p38 MAPK signaling pathways, which might be the molecular mechanism for the anti-atherosclerotic effect of curcumin.
Keywords: EMMPRIN; MMP-9; atherosclerosis; curcumin; macrophage; oxLDL.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Curcumin inhibits EMMPRIN and MMP-9 expression through AMPK-MAPK and PKC signaling in PMA induced macrophages.J Transl Med. 2014 Sep 21;12:266. doi: 10.1186/s12967-014-0266-2. J Transl Med. 2014. PMID: 25241044 Free PMC article.
-
Visfatin/PBEF/Nampt induces EMMPRIN and MMP-9 production in macrophages via the NAMPT-MAPK (p38, ERK1/2)-NF-κB signaling pathway.Int J Mol Med. 2011 Apr;27(4):607-15. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2011.621. Epub 2011 Feb 15. Int J Mol Med. 2011. PMID: 21327328
-
Suppression of oxLDL-induced MMP-9 and EMMPRIN expression by berberine via inhibition of NF-κB activation in human THP-1 macrophages.Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012 Jan;295(1):78-86. doi: 10.1002/ar.21489. Epub 2011 Dec 5. Anat Rec (Hoboken). 2012. PMID: 22140092
-
Berberine Regulated miR150-5p to Inhibit P2X7 Receptor, EMMPRIN and MMP-9 Expression in oxLDL Induced Macrophages.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Apr 20;12:639558. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.639558. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33959010 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin and cancer biology: Focusing regulatory effects in different signalling pathways.Phytother Res. 2021 Sep;35(9):4913-4929. doi: 10.1002/ptr.7121. Epub 2021 Apr 9. Phytother Res. 2021. PMID: 33837579 Review.
Cited by
-
New Concepts on the Pathophysiology of Acute Coronary Syndrome.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Apr 17;24(4):112. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2404112. eCollection 2023 Apr. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2023. PMID: 39076267 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Role of MMP-9 and MMP-9 Inhibition in Different Types of Thyroid Carcinoma.Molecules. 2023 Apr 25;28(9):3705. doi: 10.3390/molecules28093705. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37175113 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidized-LDL inhibits testosterone biosynthesis by affecting mitochondrial function and the p38 MAPK/COX-2 signaling pathway in Leydig cells.Cell Death Dis. 2020 Aug 14;11(8):626. doi: 10.1038/s41419-020-02751-z. Cell Death Dis. 2020. PMID: 32796811 Free PMC article.
-
Curcumin as a Natural Remedy for Atherosclerosis: A Pharmacological Review.Molecules. 2021 Jul 1;26(13):4036. doi: 10.3390/molecules26134036. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 34279384 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease: Non-invasive assessment of cardiovascular risk.World J Diabetes. 2021 Jul 15;12(7):975-996. doi: 10.4239/wjd.v12.i7.975. World J Diabetes. 2021. PMID: 34326949 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Belovici M. I., Pandele G. I. (2008). [Arterial media calcification in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus]. Rev. Med. Chir. Soc. Med. Nat. Iasi 112, 21–34. - PubMed
-
- Bharti A. C., Donato N., Singh S., Aggarwal B. B. (2003). Curcumin (diferuloylmethane) down-regulates the constitutive activation of nuclear factor-κB and IκBα kinase in human multiple myeloma cells, leading to suppression of proliferation and induction of apoptosis. Blood 101, 1053–1062. 10.1182/blood-2002-05-1320 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

