Prostaglandin E2 As a Modulator of Viral Infections
- PMID: 28261111
- PMCID: PMC5306375
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00089
Prostaglandin E2 As a Modulator of Viral Infections
Abstract
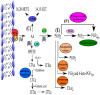
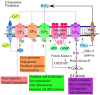
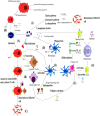
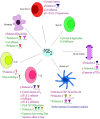
Viral infections are a major cause of infectious diseases worldwide. Inflammation and the immune system are the major host defenses against these viral infection. Prostaglandin E2 (PGE2), an eicosanoid generated by cyclooxygenases, has been shown to modulate inflammation and the immune system by regulating the expression/concentration of cytokines. The effect of PGE2 on viral infection and replication is cell type- and virus-family-dependent. The host immune system can be modulated by PGE2, with regards to immunosuppression, inhibition of nitrogen oxide (NO) production, inhibition of interferon (IFN) and apoptotic pathways, and inhibition of viral receptor expression. Furthermore, PGE2 can play a role in viral infection directly by increasing the production and release of virions, inhibiting viral binding and replication, and/or stimulating viral gene expression. PGE2 may also have a regulatory role in the induction of autoimmunity and in signaling via Toll-like receptors. In this review the known effects of PGE2 on the pathogenesis of various infections caused by herpes simplex virus, rotavirus, influenza A virus and human immunodeficiency virus as well the therapeutic potential of PGE2 are discussed.
Keywords: immunity; inflammation; prostaglandin E2; therapeutic agents; viral infection.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Activation of COX-2/PGE2 Promotes Sapovirus Replication via the Inhibition of Nitric Oxide Production.J Virol. 2017 Jan 18;91(3):e01656-16. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01656-16. Print 2017 Feb 1. J Virol. 2017. PMID: 27881647 Free PMC article.
-
Prostaglandin E2 reduces the release and infectivity of new cell-free virions and cell-to-cell HIV-1 transfer.PLoS One. 2014 Feb 25;9(2):e85230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0085230. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24586238 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted prostaglandin E2 inhibition enhances antiviral immunity through induction of type I interferon and apoptosis in macrophages.Immunity. 2014 Apr 17;40(4):554-68. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Apr 10. Immunity. 2014. PMID: 24726877
-
Candida albicans-enteric viral interactions-The prostaglandin E2 connection and host immune responses.iScience. 2022 Dec 24;26(1):105870. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105870. eCollection 2023 Jan 20. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36647379 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-hydrolyzed in digestive tract and blood natural L-carnosine peptide ("bioactivated Jewish penicillin") as a panacea of tomorrow for various flu ailments: signaling activity attenuating nitric oxide (NO) production, cytostasis, and NO-dependent inhibition of influenza virus replication in macrophages in the human body infected with the virulent swine influenza A (H1N1) virus.J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013;24(1):1-26. doi: 10.1515/jbcpp-2012-0037. J Basic Clin Physiol Pharmacol. 2013. PMID: 23425625 Review.
Cited by
-
Superior protective effects of PGE2 priming mesenchymal stem cells against LPS-induced acute lung injury (ALI) through macrophage immunomodulation.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Mar 22;14(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03277-9. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 36949464 Free PMC article.
-
Pathogens MenTORing Macrophages and Dendritic Cells: Manipulation of mTOR and Cellular Metabolism to Promote Immune Escape.Cells. 2020 Jan 9;9(1):161. doi: 10.3390/cells9010161. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31936570 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Retrospective Observational Study of Hypoxic COVID-19 Patients Treated with Immunomodulatory Drugs in a Tertiary Care Hospital.Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020 Nov;24(11):1020-1027. doi: 10.5005/jp-journals-10071-23599. Indian J Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 33384506 Free PMC article.
-
Vascular fibrosis and extracellular matrix remodelling in post-COVID 19 conditions.Infect Med (Beijing). 2024 Oct 19;3(4):100147. doi: 10.1016/j.imj.2024.100147. eCollection 2024 Dec. Infect Med (Beijing). 2024. PMID: 39649442 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Home as the new frontier for the treatment of COVID-19: the case for anti-inflammatory agents.Lancet Infect Dis. 2023 Jan;23(1):e22-e33. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(22)00433-9. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Lancet Infect Dis. 2023. PMID: 36030796 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Alberts B., Johnson A., Lewis J., Raff M., Roberts K., Walter P. (eds.) (2002). Helper T Cells and lymphocyte activation, in Molecular Biology of the Cell (New York, NY: Garland Science; ).
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

