Technical advances in global DNA methylation analysis in human cancers
- PMID: 28261325
- PMCID: PMC5331624
- DOI: 10.1186/s13036-017-0052-9
Technical advances in global DNA methylation analysis in human cancers
Abstract
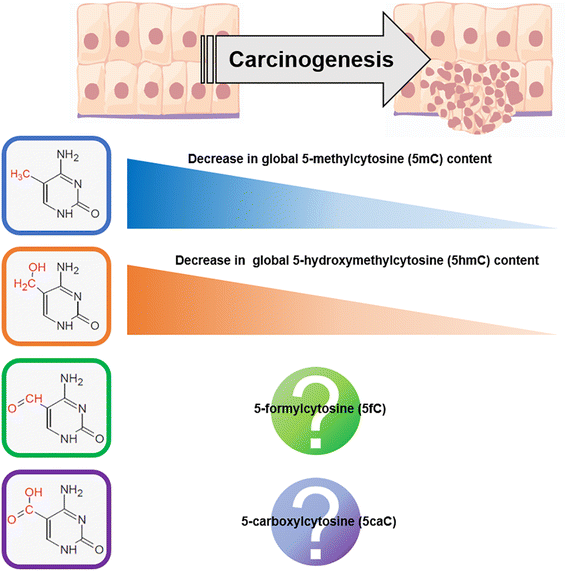
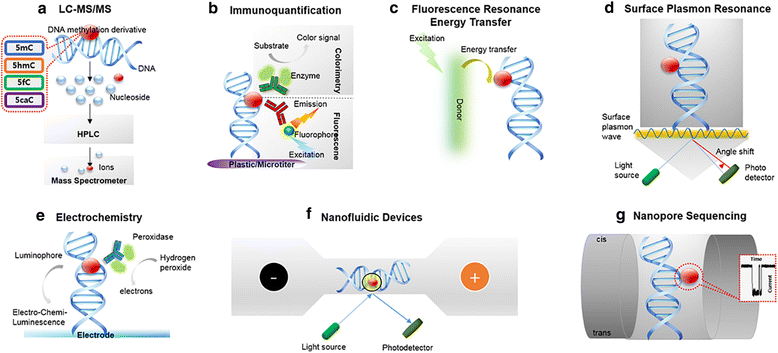
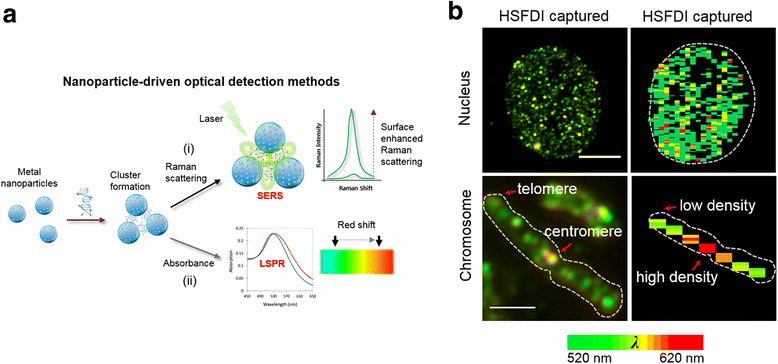
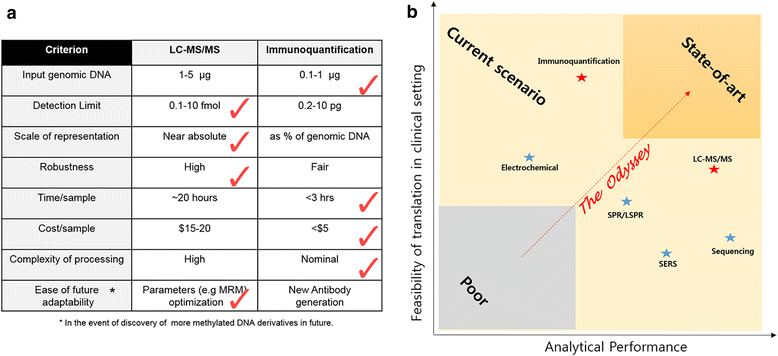
Prototypical abnormalities of genome-wide DNA methylation constitute the most widely investigated epigenetic mechanism in human cancers. Errors in the cellular machinery to faithfully replicate the global 5-methylcytosine (5mC) patterns, commonly observed during tumorigenesis, give rise to misregulated biological pathways beneficial to the rapidly propagating tumor mass but deleterious to the healthy tissues of the affected individual. A growing body of evidence suggests that the global DNA methylation levels could serve as utilitarian biomarkers in certain cancer types. Important breakthroughs in the recent years have uncovered further oxidized derivatives of 5mC - 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC), 5-formylcytosine (5fC) and 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC), thereby expanding our understanding of the DNA methylation dynamics. While the biological roles of these epigenetic derivatives are being extensively characterized, this review presents a perspective on the opportunity of innovation in the global methylation analysis platforms. While multiple methods for global analysis of 5mC in clinical samples exist and have been reviewed elsewhere, two of the established methods - Liquid Chromatography coupled with mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) and Immunoquantification have successfully evolved to include the quantitation of 5hmC, 5fC and 5caC. Although the analytical performance of LC-MS/MS is superior, the simplicity afforded by the experimental procedure of immunoquantitation ensures it's near ubiquity in clinical applications. Recent developments in spectroscopy, nanotechnology and sequencing also provide immense promise for future evaluations and are discussed briefly. Finally, we provide a perspective on the current scenario of global DNA methylation analysis tools and present suggestions to develop the next generation toolset.
Keywords: 5-carboxylcytosine (5caC); 5-formylcytosine (5fC); 5-hydroxymethylcytosine (5hmC); 5-methylcytosine (5mC); Immunoquantitation; LC-MS/MS; Next generation toolset.
Figures
References
-
- Mendel G . Gregor Mendel’s Experiments on plant hybrids: a guided study. New Brunswick: Rutgers University Press; 1993.
-
- Crick FH. On protein synthesis. Symp Soc Exp Biol. 1958;12:138–63. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

