Odd couple: The unexpected partnership of glucocorticoid hormones and cysteinyl-leukotrienes in the extrinsic regulation of murine bone-marrow eosinopoiesis
- PMID: 28261551
- PMCID: PMC5316900
- DOI: 10.5493/wjem.v7.i1.11
Odd couple: The unexpected partnership of glucocorticoid hormones and cysteinyl-leukotrienes in the extrinsic regulation of murine bone-marrow eosinopoiesis
Abstract
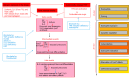
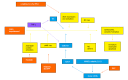
Granulopoiesis in murine bone-marrow is regulated by both intrinsic and extrinsic factors (including hormones, drugs, inflammatory mediators and cytokines). Eosinophils, a minor subpopulation of circulating leukocytes, which remains better understood in its contributions to tissue injury in allergic disease than in its presumably beneficial actions in host defense, provide a striking example of joint regulation of granulopoiesis within murine bone-marrow by all of these classes of extrinsic factors. We first described the upregulation of eosinopoiesis in bone-marrow of allergen-sensitized mice following airway allergen challenge. Over the last decade, we were able to show a critical role for endogenous glucocorticoid hormones and cytokines in mediating this phenomenon through modification of cytokine effects, thereby supporting a positive association between stress hormones and allergic reactions. We have further shown that cysteinyl-leukotrienes (CysLT), a major proinflammatory class of lipid mediators, generated through the 5-lipoxygenase pathway, upregulate bone-marrow eosinopoiesis in vivo and in vitro. CysLT mediate the positive effects of drugs (indomethacin and aspirin) and of proallergic cytokines (eotaxin/CCL11 and interleukin-13) on in vitro eosinopoiesis. While these actions of endogenous GC and CysLT might seem unrelated and even antagonistic, we demonstrated a critical partnership of these mediators in vivo, shedding light on mechanisms linking stress to allergy: GC are required for CysLT-mediated upregulation of bone-marrow eosinopoiesis in vivo, but also attenuate subsequent ex vivo responses to CysLT. GC and CysLT therefore work together to induce eosinophilia, but through subtle regulatory mechanisms also limit the magnitude of subsequent bone-marrow responses to allergen.
Keywords: Bone marrow; Eosinophil; Glucocorticoid; Leukotriene; Stress.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest statement: The authors declare no conflicting interests exist related to this article.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allergen challenge-induced changes in bone-marrow responses to leukotriene D4, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cytokines.Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020 Jun;42(3):199-210. doi: 10.1080/08923973.2020.1733598. Epub 2020 Mar 3. Immunopharmacol Immunotoxicol. 2020. PMID: 32122206
-
Essential roles of endogenous glucocorticoids and TNF/TNFR1 in promoting bone-marrow eosinopoiesis in ovalbumin-sensitized, airway-challenged mice.Life Sci. 2014 Jan 14;94(1):74-82. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2013.11.006. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Life Sci. 2014. PMID: 24239638
-
Cysteinyl-leukotriene type 1 receptors transduce a critical signal for the up-regulation of eosinophilopoiesis by interleukin-13 and eotaxin in murine bone marrow.J Leukoc Biol. 2010 May;87(5):885-93. doi: 10.1189/jlb.1108709. Epub 2010 Mar 10. J Leukoc Biol. 2010. PMID: 20219953 Free PMC article.
-
The effects of allergen and anti-allergic drugs on murine hemopoietic cells: moving targets, unusual mechanisms, and changing paradigms.Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2003 Dec;2(4):329-37. doi: 10.2174/1568010033484089. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 2003. PMID: 14561152 Review.
-
Cysteinyl leukotrienes and their receptors: molecular and functional characteristics.Pharmacology. 2010;85(6):336-49. doi: 10.1159/000312669. Epub 2010 Jun 2. Pharmacology. 2010. PMID: 20516735 Review.
References
-
- Metcalf D. Some general aspects of hemtopoietic cell development. In Zon L (Ed.). Hematopoiesis. A developmental approach. Oxford University Press. New York: Oxford; 2001. pp. 3–14.
-
- Kobayashi H, Suda T, Takubo K. How hematopoietic stem/progenitors and their niche sense and respond to infectious stress. Exp Hematol. 2016;44:92–100. - PubMed
-
- Takizawa H, Boettcher S, Manz MG. Demand-adapted regulation of early hematopoiesis in infection and inflammation. Blood. 2012;119:2991–3002. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

