Impact of heat shock step on bacterial transformation efficiency
- PMID: 28261629
- PMCID: PMC5326489
Impact of heat shock step on bacterial transformation efficiency
Abstract
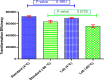
CaCl2 treatment followed by heat shock is the most common method for artificial transformation. Here, the cells were transformed using CaCl2 treatment either with heat shock (standard protocol) or without heat shock (lab protocol) to comprehend the difference in transformation efficiency. The BL21 strain of Escherichia coli (E. coli) was being susceptible using CaCl2 treatment. Some Cells were kept at -80 oC while the others were kept at 4 ˚C. Afterwards the susceptible cells were transformed using either standard or lab protocol. The transformation efficiency between cells experienced heat shock and those were not influenced by heat shock was almost the same. Moreover, regardless of transformation protocol, the cells kept at 4 ˚C were transformed more efficiently in compared to those were kept at -80 oC.
Keywords: Artificial transformation; E. coli; Heat shock; Transformation efficiency.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Vibration and glycerol-mediated plasmid DNA transformation for Escherichia coli.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013 Nov;348(1):74-8. doi: 10.1111/1574-6968.12247. Epub 2013 Sep 19. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2013. PMID: 24004211
-
Analysis of comparative efficiencies of different transformation methods of E. coli using two common plasmid vectors.Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2009 Oct;46(5):395-400. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2009. PMID: 20027870
-
Capillary-composited microfluidic device for heat shock transformation of Escherichia coli.J Biosci Bioeng. 2011 Oct;112(4):373-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2011.06.004. Epub 2011 Jul 16. J Biosci Bioeng. 2011. PMID: 21763195
-
The heat shock response of Escherichia coli.Int J Food Microbiol. 2000 Apr 10;55(1-3):3-9. doi: 10.1016/s0168-1605(00)00206-3. Int J Food Microbiol. 2000. PMID: 10791710 Review.
-
Microbial molecular chaperones.Adv Microb Physiol. 2001;44:93-140. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(01)44012-4. Adv Microb Physiol. 2001. PMID: 11407116 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel method for DNA delivery into bacteria using cationic copolymers.Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021 Apr 2;54(5):e10743. doi: 10.1590/1414-431X202010743. eCollection 2021. Braz J Med Biol Res. 2021. PMID: 33825778 Free PMC article.
-
A Structural Bioinformatics-Guided Study of Adenosine Triphosphate-Binding Cassette (ABC) Transporters and Their Substrates.Membranes (Basel). 2025 Jan 10;15(1):20. doi: 10.3390/membranes15010020. Membranes (Basel). 2025. PMID: 39852261 Free PMC article.
-
Development and mechanism exploration of a quantitative model for Escherichia coli transformation efficiency based on ultrasonic power.Ultrason Sonochem. 2024 Dec;111:107132. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2024.107132. Epub 2024 Oct 28. Ultrason Sonochem. 2024. PMID: 39481288 Free PMC article.
-
Phenotypic and molecular characterization of extended spectrum- and metallo- beta lactamase producing Pseudomonas aeruginosa clinical isolates from Egypt.Infection. 2024 Dec;52(6):2399-2414. doi: 10.1007/s15010-024-02297-8. Epub 2024 Jun 2. Infection. 2024. PMID: 38824475 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Nε-Acryloyllysine Piperazides on the Conformational Dynamics of Transglutaminase 2.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1650. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021650. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675164 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chen I, Dubnau D. DNA uptake during bacterial transformation. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2004;2:241–249. - PubMed
-
- Panja S, Saha S, Jana B, Basu T. Role of membrane potential on artificial transformation of E coli with plasmid DNA. J Biotechnol. 2006;127:14–20. - PubMed
-
- Divya Prakash G, Anish RV, Jagadeesh G, Chakravortty D. Bacterial transformation using micro-shock waves. Anal Biochem. 2011;419:292–301. - PubMed
-
- Inoue H, Nojima H, Okayama H. High efficiency transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. Gene. 1990;96:23–28. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous